Identification of the iduronate-2-sulfatase proteome in wild-type mouse brain
- PMID: 31193135
- PMCID: PMC6517578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01667
Identification of the iduronate-2-sulfatase proteome in wild-type mouse brain
Abstract
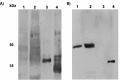
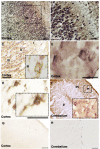
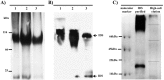
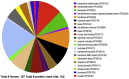
Iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) is a lysosomal enzyme involved in the metabolism of the glycosaminoglycans heparan (HS) and dermatan (DS) sulfate. Mutations on IDS gene produce mucopolysaccharidosis II (MPS II), characterized by the lysosomal accumulation of HS and DS, leading to severe damage of the central nervous system (CNS) and other tissues. In this study, we used a neurochemistry and proteomic approaches to identify the brain distribution of IDS and its interacting proteins on wild-type mouse brain. IDS immunoreactivity showed a robust staining throughout the entire brain, suggesting an intracellular reactivity in nerve cells and astrocytes. By using affinity purification and mass spectrometry we identified 187 putative IDS partners-proteins, mainly hydrolases, cytoskeletal proteins, transporters, transferases, oxidoreductases, nucleic acid binding proteins, membrane traffic proteins, chaperons and enzyme modulators, among others. The interactions with some of these proteins were predicted by using bioinformatics tools and confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation analysis and Blue Native PAGE. In addition, we identified cytosolic IDS-complexes containing proteins from predicted highly connected nodes (hubs), with molecular functions including catalytic activity, redox balance, binding, transport, receptor activity and structural molecule activity. The proteins identified in this study would provide new insights about IDS physiological role into the CNS and its potential role in the brain-specific protein networks.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Bioinformatics; Biotechnology; Cell biology; Computational biology.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Iduronate-2-sulfatase interactome: validation by yeast two-hybrid assay.Heliyon. 2022 Mar 1;8(3):e09031. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09031. eCollection 2022 Mar. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35284671 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in MPS I and MPS II Disease Manifestations.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 23;22(15):7888. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157888. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid heparan sulfate as a biomarker of neuropathology in a murine model of mucopolysaccharidosis type II using high-sensitivity LC/MS/MS.Mol Genet Metab. 2018 Sep;125(1-2):53-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.07.013. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2018. PMID: 30064964
-
Prevention of Neurocognitive Deficiency in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II Mice by Central Nervous System-Directed, AAV9-Mediated Iduronate Sulfatase Gene Transfer.Hum Gene Ther. 2017 Aug;28(8):626-638. doi: 10.1089/hum.2016.184. Epub 2017 May 5. Hum Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 28478695
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome): Clinical and biochemical aspects of the disease and approaches to its diagnosis and treatment.Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 2020;77:71-117. doi: 10.1016/bs.accb.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 2020. PMID: 33004112 Review.
Cited by
-
Iduronate-2-sulfatase interactome: validation by yeast two-hybrid assay.Heliyon. 2022 Mar 1;8(3):e09031. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09031. eCollection 2022 Mar. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35284671 Free PMC article.
-
4-Ethylphenol-fluxes, metabolism and excretion of a gut microbiome derived neuromodulator implicated in autism.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Oct 12;10:1267754. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1267754. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37900921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in MPS I and MPS II Disease Manifestations.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 23;22(15):7888. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157888. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and mechanisms of the GPCR adaptor protein Norbin.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Aug 31;51(4):1545-1558. doi: 10.1042/BST20221349. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37503670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics in neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorders.Mol Omics. 2022 May 11;18(4):256-278. doi: 10.1039/d2mo00004k. Mol Omics. 2022. PMID: 35343995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neufeld E., Muenzer J. In: Valle D., editor. Vol. III. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2014. (The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Diseases).
-
- Scarpa M. In: GeneReviews(R) Pagon R.A., editor. 1993.
-
- Hamano K., Hayashi M., Shioda K., Fukatsu R., Mizutani S. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration in mucopolysaccharidoses II and IIIB: analysis of human brain tissue. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;115:547–559. - PubMed
-
- Neufeld E.F. Lysosomal storage diseases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1991;60:257–280. - PubMed
-
- Bellettato C.M., Scarpa M. Pathophysiology of neuropathic lysosomal storage disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010;33:347–362. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

