De novo production of aromatic m-cresol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediated by heterologous polyketide synthases combined with a 6-methylsalicylic acid decarboxylase
- PMID: 31193192
- PMCID: PMC6520567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mec.2019.e00093
De novo production of aromatic m-cresol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediated by heterologous polyketide synthases combined with a 6-methylsalicylic acid decarboxylase
Abstract
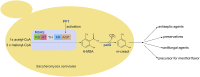
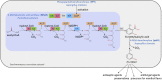
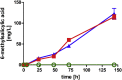
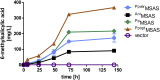
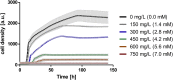
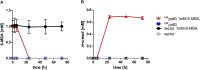
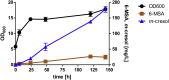
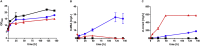
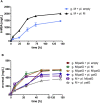
As a flavor and platform chemical, m-cresol (3-methylphenol) is a valuable industrial compound that currently is mainly synthesized by chemical methods from fossil resources. In this study, we present the first biotechnological de novo production of m-cresol from sugar in complex yeast extract-peptone medium with the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A heterologous pathway based on the decarboxylation of the polyketide 6-methylsalicylic acid (6-MSA) was introduced into a CEN.PK yeast strain. For synthesis of 6-MSA, expression of different variants of 6-MSA synthases (MSASs) were compared. Overexpression of codon-optimized MSAS from Penicillium patulum together with activating phosphopantetheinyl transferase npgA from Aspergillus nidulans resulted in up to 367 mg/L 6-MSA production. Additional genomic integration of the genes had a strongly promoting effect and 6-MSA titers reached more than 2 g/L. Simultaneous expression of 6-MSA decarboxylase patG from A. clavatus led to the complete conversion of 6-MSA and production of up to 589 mg/L m-cresol. As addition of 450-750 mg/L m-cresol to yeast cultures nearly completely inhibited growth our data suggest that the toxicity of m-cresol might be the limiting factor for higher production titers.
Keywords: 6-Methylsalicylic acid decarboxylase; 6-Methylsalicylic acid synthase; 6-methylsalicylic acid decarboxylase, PatG; 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase, MSAS; 6-methylsalicylic acid, 6-MSA; Acyl carrier protein, ACP; Acyltransferase, AT; Codon-optimization; Polyketide synthase; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; ketoreductase, KR; ketosynthase, KS; m-Cresol; optical density, OD; phosphopantetheinyl transferase, PPT; polyketide synthase, PKS; thioester hydrolase, TH.
Figures
References
-
- Beck J., Ripka S., Siegner A., Schiltz E., Schweizer E. The multifunctional 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase gene of Penicillium patulum. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990;192:487–498. - PubMed
-
- Berger R.G. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2007. Flavours and Fragrances Chemistry, Bioprocessing and Sustainability.
-
- Bruder S., Reifenrath M., Thomik T., Boles E., Herzog K. Parallelised online biomass monitoring in shake flasks enables efficient strain and carbon source dependent growth characterisation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Cell Factories. 2016;15:127. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0526-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

