Positive correlation between fasting plasma glucagon and serum C-peptide in Japanese patients with diabetes
- PMID: 31193194
- PMCID: PMC6520599
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01715
Positive correlation between fasting plasma glucagon and serum C-peptide in Japanese patients with diabetes
Abstract
Aims: Glucagon plays pivotal roles in systemic glucose homeostasis mainly by promoting hepatic glucose output. Using a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), we evaluated fasting plasma glucagon levels in hospitalized patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and assessed the relationships between glucagon levels and various clinical parameters.
Methods: We enrolled adult Japanese diabetes patients admitted to Osaka University Medical Hospital for glycemic control between July 2017 and May 2018 in this study. After patients had fasted for 12 h, blood samples were obtained and plasma glucagon levels were measured using a sandwich ELISA.
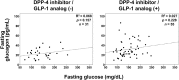
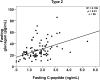
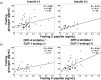
Results: Total 107 patients participated in the study. The mean fasting plasma glucagon level of patients with acute onset type 1 diabetes was significantly lower than that of patients with type 2 diabetes (p < 0.05). Plasma glucagon levels were not significantly correlated with plasma glucose levels in patients with type 1 diabetes or in patients with type 2 diabetes. Multiple regression analysis indicated that fasting glucagon levels were independently and significantly correlated with fasting serum C-peptide levels in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that insulin and glucagon secretion are balanced in the fasting state in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Metabolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fasting serum total bile acid levels are associated with insulin sensitivity, islet β-cell function and glucagon levels in response to glucose challenge in patients with type 2 diabetes.Endocr J. 2020 Nov 28;67(11):1107-1117. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0201. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Endocr J. 2020. PMID: 32684527
-
Basal glucagon hypersecretion and response to oral glucose load in prediabetes and mild type 2 diabetes.Endocr J. 2019 Aug 29;66(8):663-675. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ18-0372. Epub 2019 May 28. Endocr J. 2019. PMID: 31142688 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma glucagon levels measured by sandwich ELISA are correlated with impaired glucose tolerance in type 2 diabetes.Endocr J. 2020 Sep 28;67(9):903-922. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0079. Epub 2020 May 23. Endocr J. 2020. PMID: 32448820
-
On the role of the gut in diabetic hyperglucagonaemia.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5340. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385175 Review.
-
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide: effects on insulin and glucagon secretion in humans.Dan Med J. 2016 Apr;63(4):B5230. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27034187 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Two Different Glucagon Assays in Healthy Individuals and Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Patients.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 18;12(3):466. doi: 10.3390/biom12030466. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327658 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between glucagon and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.World J Hepatol. 2025 Jun 27;17(6):104693. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.104693. World J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40606916 Free PMC article.
-
Lowest Glucagon/Highest C-Peptide in Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Clinical Utility in Monitoring Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Apr 17;17:1769-1780. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S459392. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38645659 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in clinical research on glucagon.Diabetol Int. 2024 Mar 23;15(3):353-361. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00705-w. eCollection 2024 Jul. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 39101175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fasting Glucagon Level in Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Its Association With Diabetes-Associated Clinical Parameters: A Study From Karachi, Pakistan.Cureus. 2021 Feb 18;13(2):e13430. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13430. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33758717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Unger R.H., Cherrington A.D. Glucagonocentric restructuring of diabetes: a pathophysiologic and therapeutic makeover. J. Clin. Investig. 2012;122:4–12. https://www.jci.org/articles/view/60016 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knop F.K., Aaboe K., Vilsbøll T., Vølund A., Holst J.J., Krarup T., Madsbad S. Impaired incretin effect and fasting hyperglucagonaemia characterizing type 2 diabetic subjects are early signs of dysmetabolism in obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012;14:500–510. - PubMed
-
- Müller W.A., Faloona G.R., Aguilar-Parada E., Unger R.H. Abnormal alpha-cell function in diabetes. Response to carbohydrate and protein ingestion. N. Engl. J. Med. 1970;283:109–115. - PubMed
-
- Kawai K., Murayama Y., Okuda Y., Yamashita K. Postprandial glucose, insulin and glucagon responses to meals with different nutrient compositions in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol. Jpn. 1987;34:745–753. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/endocrj1954/34/5/34_5_745/_article - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

