Novel 3-((2-chloroquinolin-3-yl)methylene)indolin-2-one derivatives produce anticancer efficacy in ovarian cancer in vitro
- PMID: 31193218
- PMCID: PMC6522656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01603
Novel 3-((2-chloroquinolin-3-yl)methylene)indolin-2-one derivatives produce anticancer efficacy in ovarian cancer in vitro
Abstract
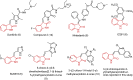
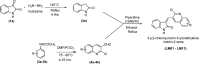
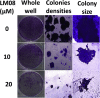
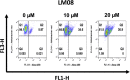
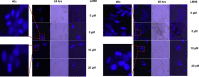
A novel series of 3-((2-chloroquinolin-3-yl)methylene)indolin-2-ones were synthesized, using the 'molecular hybridization approach' and evaluated for anticancer efficacy. Eleven 3-((2-chloroquinolin-3-yl)methylene)indolin-2-ones (LM01 to LM11) were synthesized and evaluated for in vitro cytotoxic efficacy in cancer (ovarian, prostate and colon) and two non-cancerous cell lines. Among the 3-((2-chloroquinolin-3-yl)methylene)indolin-2-one derivatives, LM08, with a 6-Cl substitution in the 3-quinolinyl moiety, had selective and potent cytotoxic efficacy in the ovarian cancer cell line A2780. Further mechanistic investigations indicated that LM08 significantly inhibited the clonogenic survival of A2780 cancer cells, which was mediated by inducing apoptosis.
Keywords: Natural product chemistry; Pharmaceutical chemistry; Pharmaceutical science.
Figures
References
-
- World Cancer Report 2014. World Health Organization; 2014. Chapter 1.1.
-
- Belal A. Design, synthesis and anticancer activity evaluation of some novel pyrrolo[1,2-a]azepine derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2014;347(7):515–522. Epub 2014/04/15PubMed PMID: 24729464. - PubMed
-
- Kurumurthy C., Veeraswamy B., Sambasiva Rao P., Santhosh Kumar G., Shanthan Rao P., Loka Reddy V. Synthesis of novel 1,2,3-triazole tagged pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine derivatives and their cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014;24(3):746–749. Epub 2014/01/16PubMed PMID: 24424132. - PubMed
-
- Wang S., Folkes A., Chuckowree I., Cockcroft X., Sohal S., Miller W. Studies on pyrrolopyrimidines as selective inhibitors of multidrug-resistance-associated protein in multidrug resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2004;47(6):1329–1338. Epub 2004/03/05PubMed PMID: 14998323. - PubMed
-
- Pakravan P., Kashanian S., Khodaei M.M., Harding F.J. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of isatin and its derivatives: from structure to activity. Pharmacol. Rep. : PR. 2013;65(2):313–335. Epub 2013/06/08. PubMed PMID: 23744416. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

