The trends in robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty: A statewide database study
- PMID: 31193224
- PMCID: PMC6522752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2019.04.020
The trends in robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty: A statewide database study
Abstract
Objective: Recent technological advancements have led to the utilization of robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty (raKA) in the operating room.
Methods: All patients who underwent knee arthroplasty from 2009 to 2013 in NYS SPARCS were reviewed. raKAs and non-raKAs were compared for utilization and institutional trends.
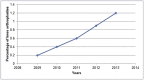
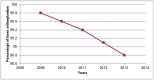
Results: Robotic-assistance increased by 500%. 80% of raKAs were performed in teaching hospitals. The trend increase was greater in teaching hospitals. Blood transfusion rates differed between raKA and non-raKA (6.6% vs. 10.9%, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: raKA utilization increased in NYS, moreso within teaching hospitals. raKA transfusion rates were lower but higher in teaching hospitals, potentially related to learning curve.
Keywords: Robotic surgery; Robotic-assisted surgery; Statewide Planning and Research Cooperative System (SPARCS), New York State (NYS); Total knee arthroplasty; Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty; Utilization trends.
Figures
References
-
- Lane N.E., Brandt K., Hawker G. OARSI-FDA initiative: defining the disease state of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(5):478–482. - PubMed
- Lane NE, Brandt K, Hawker G, et al. OARSI-FDA initiative: Defining the disease state of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2011;19(5):478-482. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2010.09.013. - PubMed
-
- Eckstein F., Burstein D., Link T.M. Quantitative MRI of cartilage and bone: degenerative changes in osteoarthritis. NMR Biomed. 2006;19(7):822–854. - PubMed
- Eckstein F, Burstein D, Link TM. Quantitative MRI of cartilage and bone: degenerative changes in osteoarthritis. NMR Biomed. 2006;19(7):822-854. doi:10.1002/nbm.1063. - PubMed
-
- Link T.M., Steinbach L.S., Ghosh S. Osteoarthritis: MR imaging findings in different stages of disease and correlation with clinical findings. Radiology. 2003;226(2):373–381. - PubMed
- Link TM, Steinbach LS, Ghosh S, et al. Osteoarthritis: MR imaging findings in different stages of disease and correlation with clinical findings. Radiology. 2003;226(2):373-381. doi:10.1148/radiol.2262012190. - PubMed
-
- Gladnick B.P., Nam D., Khamaisy S., Paul S., Pearle A.D. Onlay tibial implants appear to provide superior clinical results in robotic unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. HSS J. 2015;11(1):43–49. - PMC - PubMed
- Gladnick BP, Nam D, Khamaisy S, Paul S, Pearle AD. Onlay Tibial Implants Appear to Provide Superior Clinical Results in Robotic Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. HSS J. 2015;11(1):43-49. doi:10.1007/s11420-014-9421-9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walker T., Gotterbarm T., Bruckner T., Merle C., Streit M.R. Return to sports, recreational activity and patient-reported outcomes after lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;23(11):3281–3287. - PubMed
- Walker T, Gotterbarm T, Bruckner T, Merle C, Streit MR. Return to sports, recreational activity and patient-reported outcomes after lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surgery, Sport Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;23(11):3281-3287. doi:10.1007/s00167-014-3111-5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources