Exogenous lipid pneumonia in old people caused by aspiration: Two case reports and literature review
- PMID: 31193250
- PMCID: PMC6522775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.100850
Exogenous lipid pneumonia in old people caused by aspiration: Two case reports and literature review
Abstract
Background: Exogenous lipoid pneumonia is a rare entity, the diagnosis is often missed or delayed.
Objective: To investigate the clinical characteristics of exogenous lipid pneumonia in elderly patients, improve the efficiency of early diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
Methods: Retrospectively analyzed the clinical information and imaging data of these 2 exogenous lipid pneumonia patients, reviewed related literature.
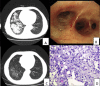
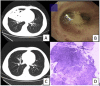
Results: Both of the 2 patients were over 60 with a history of gastrointestinal diseases. The clinical presentation is nonspecific. Chest CT showed many different manifestations. Histopathology analysis revealed the accumulation of lipid carrying macrophages, vacuolar cells and inflammation. A literature review indicated that 25 previous cases of exogenous lipid pneumonia were caused by aspiration. The most common site of the lesion was located in right lung, while mineral oil was the most common substances. We sought to discuss the patient's treatment and the corresponding outcomes.
Conclusion: The diagnosis of lipid pneumonia's mainly depends on medical history and histopathological morphology. The standard treatment for exogenous lipid pneumonia was composed of antibiotics, steroid, bronchoscopic lavage and a regular follow-up.
Keywords: Antibiotic; Chest CT; Exogenous lipid pneumonia; Pathology; Steroid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Exogenous lipid pneumonia with hyperpyrexia: a case report].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Oct 18;50(5):921-923. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30337759 Chinese.
-
Exogenous Lipoid Pneumonia Complicated by Mineral Oil Aspiration in a Patient With Chronic Constipation: A Case Report and Review.Cureus. 2020 Jul 20;12(7):e9294. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9294. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32832291 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of 12 cases of exogenous lipoid pneumonia confirmed by pathology].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 12;40(6):445-449. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2017.06.010. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28592028 Chinese.
-
Lipoid pneumonia: an overview.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010 Dec;4(6):799-807. doi: 10.1586/ers.10.74. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010. PMID: 21128754 Review.
-
[Exogenous lipoid pneumonia: a simple diagnosis?].Rev Med Liege. 2005 Oct;60(10):799-804. Rev Med Liege. 2005. PMID: 16358668 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Shine like gold and sparkle like glitter: Three cases of lipoid pneumonia.Respir Med Case Rep. 2021 Mar 9;33:101380. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2021.101380. eCollection 2021. Respir Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33777689 Free PMC article.
-
MCC950 Ameliorates Acute Exogenous Lipoid Pneumonia Induced by Sewing Machine Oil in Rats via the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway.In Vivo. 2023 Nov-Dec;37(6):2533-2542. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13361. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 37905651 Free PMC article.
-
Fever and dyspnoea in a tracheostomised patient.Breathe (Sheff). 2020 Dec;16(4):200115. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0115-2020. Breathe (Sheff). 2020. PMID: 33447286 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of exogenous lipoid pneumonia.Tunis Med. 2025 Feb 5;103(2):212-216. doi: 10.62438/tunismed.v103i2.5261. Tunis Med. 2025. PMID: 40096721 Free PMC article. French.
-
Acute exogenous lipoid pneumonia leading to severe ARDS: a case report.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03780-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40604803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron S.E., Haramati L.B. Radiological and clinical findings in acute and chronic exogenous lipoid pneumonia. J. Thorac. Imaging. 2003;18:217–224. [PubMed:14561906] - PubMed
- Baron SE,Haramati LB.Radiological and clinical findings in acute and chronic exogenous lipoid pneumonia.J Thorac Imaging. 2003;18:217-224. [PubMed:14561906] - PubMed
-
- Gondouin A., Manzoni P., Ranfaing E. Exogenous lipid pneumonia: a retrospective multicentre study of 44 cases in France. Eur. Respir. J. 1996;9:1463–1469. [PubMed:8836660] - PubMed
- Gondouin A, Manzoni P, Ranfaing E, et al. Exogenous lipid pneumonia: a retrospective multicentre study of 44 cases in France.Eur Respir J.1996; 9: 1463-1469. [PubMed:8836660] - PubMed
-
- Salgado I.A., Santos C.C., Salgado J.V. Exogenous lipoid pneumonia in children: a disease to be reminded of. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2012;58:135–137. [PubMed:22569605] - PubMed
- Salgado IA,Santos CC,Salgado JV,et al. Exogenous lipoid pneumonia in children: a disease to be reminded of.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) .2012;58:135-137. [PubMed:22569605] - PubMed
-
- Yokohori N., Taira M., Kameyama S. Acute form of exogenous lipoid pneumonia caused by inhalation of liquid paraffin in a fire-eater. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2002 Jul;40(7):588–593. [PubMed:12382424] - PubMed
- Yokohori N, Taira M, Kameyama S, et al. Acute form of exogenous lipoid pneumonia caused by inhalation of liquid paraffin in a fire-eater. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2002 Jul;40(7):588-593. [PubMed:12382424] - PubMed
-
- Ohwada A., Yoshioka Y., Shimanuki Y. Exogenous lipoid pneumonia following ingestion of liquid paraffin. Intern. Med. 2002;41(6):483–486. [PubMed:12135184] - PubMed
- Ohwada A, Yoshioka Y, Shimanuki Y, et al. Exogenous lipoid pneumonia following ingestion of liquid paraffin. Internal Medicine.2002, 41(6):483-486.[PubMed:12135184] - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

