Nasal nitric oxide is a useful biomarker for acute unilateral maxillary sinusitis in pediatric allergic rhinitis: A prospective observational cohort study
- PMID: 31193296
- PMCID: PMC6526296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.waojou.2019.100027
Nasal nitric oxide is a useful biomarker for acute unilateral maxillary sinusitis in pediatric allergic rhinitis: A prospective observational cohort study
Abstract
Background: Nasal nitric oxide (nNO) could be a biomarker for nasal passage inflammation and sinus ostial patency. We have aimed to investigate the nNO concentration and the effect of antibiotic therapy in children with perennial allergic rhinitis (PAR) children with/without acute bacterial sinusitis.
Methods: We enrolled a cohort of 90 and 31 children with PAR, without and with acute unilateral maxillary sinusitis, and 79 normal children. Acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis was diagnosed based on clinical signs and symptoms, radiographic examination and nasal fibroendoscopy. Rhinitis control assessment test (RCAT), rhinomanometry, nNO and fractional exhaled NO (FENO) measurements were performed before and 2 weeks after antibiotic therapy.
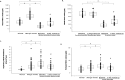
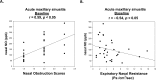
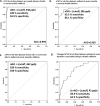
Results: We found significantly higher mean nNO levels, FENO values, and total nasal resistance in children with PAR than in normal children (p < 0.05). Acute unilateral maxillary sinusitis was associated with lower lesion-side nNO levels, higher FENO values, total nasal resistance, and poor RCAT scores (p < 0.05). In multivariate analysis, age, IgE, and acute maxillary sinusitis were significant factors influencing nNO levels in children with PAR. The lesion-side nNO levels, FENO values, total nasal resistance, and RCAT scores were reversed after antibiotic therapy (p < 0.05). The lesion-side nNO levels were significantly correlated to nasal obstructive scores (r = 0.59, p < 0.05) and expiratory nasal resistance (r = -0.54, p < 0.05) in the acute maxillary sinusitis. A cut-off nNO value of 538 ppb showed 100% sensitivity and 94.9% specificity, to predict PAR from normal children. An nNO value of 462 ppb showed 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity to discriminate between the lesion-side and the unaffected sinus-side in PAR children with acute unilateral maxillary sinusitis.
Conclusions: We conclude that the obstruction of NO from the sinus into the nasal passage is the likely explanation for the decreased lesion-side nNO levels in acute unilateral maxillary sinusitis. nNO is a non-invasive biomarker with high sensitivity to diagnose and monitor treatment responses of PAR patients with acute rhinosinusitis. Both nNO and FENO levels return to baseline following antibiotic therapy, supporting the "one airway one disease" concept.
Keywords: ARIA, Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma; Der f, Dermatophagoides farinae; Der p, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; FENO, Fractional Exhaled NO; NO, Nitric oxide; RCAT, Rhinitis control assessment test; nNO, Nasal nitric oxide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical application of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide levels for the assess eosinophilic inflammation of allergic rhinitis among children.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Apr;10(4):746-753. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-314. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34012824 Free PMC article.
-
Application of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in control evaluation of bronchial asthma and diagnosis of allergic rhinitis in children.Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jan 15;24(1):90-95. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2108091. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35177182 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Nasal Nitric Oxide in Children: A Review of Current Outreach in Pediatric Respiratory Medicine.Children (Basel). 2023 Oct 9;10(10):1671. doi: 10.3390/children10101671. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Airway Nitric Oxide in Children with HDM-Induced Allergic Rhinitis.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2022 May;36(3):360-366. doi: 10.1177/19458924211064407. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2022. PMID: 34879740
-
Nasal Nitric Oxide as a Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Sinonasal Inflammatory Diseases: A Review of the Literature.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2023 Apr;132(4):460-469. doi: 10.1177/00034894221093890. Epub 2022 May 12. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2023. PMID: 35549446 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical application of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide levels for the assess eosinophilic inflammation of allergic rhinitis among children.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Apr;10(4):746-753. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-314. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34012824 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Utility Of The Exhaled Nitric Oxide (NO) Measurement With Portable Devices In The Management Of Allergic Airway Inflammation And Asthma.J Asthma Allergy. 2019 Oct 7;12:331-341. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S190489. eCollection 2019. J Asthma Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31632093 Free PMC article.
-
Application of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in control evaluation of bronchial asthma and diagnosis of allergic rhinitis in children.Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jan 15;24(1):90-95. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2108091. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35177182 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Nasal Nitric Oxide in Children: A Review of Current Outreach in Pediatric Respiratory Medicine.Children (Basel). 2023 Oct 9;10(10):1671. doi: 10.3390/children10101671. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nasal nitric oxide measurement in allergic rhinitis and non-allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2024 Apr;44(2):100-112. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2634. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2024. PMID: 38651552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Voynow J.A., Montpetit A.J. Nasal NO as a biomarker: don't say NO to the many challenges of translational medicine. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015;50:100–102. - PubMed
- Voynow JA, Montpetit AJ. Nasal NO as a biomarker: don't say NO to the many challenges of translational medicine. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015;50:100-102. - PubMed
-
- Manna A., Montella S., Maniscalco M., Maglione M., Santamaria F. Clinical application of nasal nitric oxide measurement in pediatric airway diseases. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015;50:85–99. - PubMed
- Manna A, Montella S, Maniscalco M, Maglione M, Santamaria F. Clinical application of nasal nitric oxide measurement in pediatric airway diseases. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015;50:85-99. - PubMed
-
- Petsky H.L., Kew K.M., Chang A.B. Exhaled nitric oxide levels to guide treatment for children with asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;11:CD011439. - PMC - PubMed
- Petsky HL, Kew KM, Chang AB. Exhaled nitric oxide levels to guide treatment for children with asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;11:CD011439. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsai Y.G., Sun H.L., Chien J.W., Chen C.Y., Lin C.H., Lin C.Y. High exhaled nitric oxide levels correlate with nonadherence in acute asthmatic children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;118:521–523. - PubMed
- Tsai YG, Sun HL, Chien JW, Chen CY, Lin CH, Lin CY. High exhaled nitric oxide levels correlate with nonadherence in acute asthmatic children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;118:521-523. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

