Branched-chain amino acids mediate resilience to chronic social defeat stress by activating BDNF/TRKB signaling
- PMID: 31193350
- PMCID: PMC6526306
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2019.100170
Branched-chain amino acids mediate resilience to chronic social defeat stress by activating BDNF/TRKB signaling
Abstract
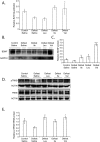
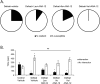
How individuals respond to chronic stress varies. Susceptible individuals ultimately develop depression; whereas resilient individuals live normally. In this study, our objective was to examine the effect of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), commonly used by athletes, on susceptibility to stress. Male C57BL/6 mice were subjected to daily defeat sessions by a CD1 aggressor, for 10 days. On day11, the behavior of mice was assessed using the social interaction test, elevated plus maze and open field. Mice received the BCAA leucine, isoleucine or valine before each defeat session. Furthermore, we examined whether BCAA regulate brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling by using a brain-permeable tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TRKB) inhibitor, ANA-12. We also tested the effect of voluntary exercise and high protein diets on susceptibility to stress. Mice exposed to chronic stress displayed increased susceptibility and social avoidance. BCAA promoted resilience to chronic stress, rescued social avoidance behaviors and increased hippocampal BDNF levels and TRKB activation. Inhibition of TRKB signaling abolished the ability of BCAA to promote resilience to stress and to rescue social avoidance. Interestingly, we found that BCAA activate the exercise-regulated PGC1a/FNDC5 pathway known to induce hippocampal BDNF signaling. Although both voluntary exercise and BCAA promoted resilience to stress, combining them did not yield synergistic effects confirming that they affect similar pathways. We also discovered that high protein diets mimic the effect of BCAA by rescuing social deficits induced by chronic stress and increase Bdnf expression in the hippocampus. Our data indicate that BCAA, exercise and high protein diets rescue susceptibility to stress by activating the hippocampal BDNF/TRKB signaling.
Keywords: BDNF; Branched chain amino acids; Chronic social defeat stress; Exercise; FNDC5; High protein diet.
Figures




References
-
- Al-Haddad R. Epigenetic changes in diabetes. Neurosci. Lett. 2016;625:64–69. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

