Interference of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatments on soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 levels in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 31193412
- PMCID: PMC6527918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plabm.2019.e00122
Interference of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor treatments on soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 levels in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor II (sTNFR2) is used as a biomarker to study cardiovascular disease (CVD) in diverse populations. TNF inhibitors (TNFi's) are a common treatment for inflammatory conditions. The objective of this study was to examine whether TNFi use impacts measured sTNFR2 levels.
Methods: We studied blood samples from a cohort of RA patients with clinical data and high sensitivity-C-reactive protein (hsCRP) measurements. To assess for interference, we tested the entire cohort for the expected positive correlation between sTNFR2 and TNFi using Pearson correlations. We then performed Pearson correlations between sTNFR2 and TNFi and sequentially removed subjects on adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab; if interference was occurring, no correlation would be observed between hsCRP and sTNFR2, and correlation would be restored by removing subjects on the treatment causing the interference.
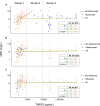
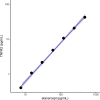
Results: We studied 190 subjects, 84.2% female, 73.4% anti-CCP positive. All subjects with sTNFR2 level exceeding measurable level were on etanercept. The expected positive correlation between hsCRP and sTNFR2 was not observed when assessing the entire cohort, r = 0.05, p = 0.51. However, the expected correlation was restored only after excluding subjects on etanercept, r = 0.46, p < 0.0001, and not adalimumab or infliximab. ELISA for sTNFR2 was performed using etanercept only and demonstrated direct binding to sTNFR2.
Conclusions: Our data identified interference between etanercept and the TNFR2 assay. Of the TNFi's, only etanercept has a TNF-binding domain modeled after TNFR2. These data should be considered when designing studies using sTNFR2 in populations where etanercept is a treatment option.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cardiovascular; High sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP); Inflammation; Rheumatoid arthritis; Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Economic Burden of Switching to a Non-Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Versus a Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Biologic Therapy among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Adv Ther. 2016 May;33(5):807-23. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0318-5. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Adv Ther. 2016. PMID: 27084724
-
Switching from an anti-TNF monoclonal antibody to soluble TNF-receptor yields better results than vice versa: An observational retrospective study of 72 rheumatoid arthritis switchers.Joint Bone Spine. 2015 Oct;82(5):330-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.01.021. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Joint Bone Spine. 2015. PMID: 25864942
-
Two-year persistence of golimumab as second-line biologic agent in rheumatoid arthritis as compared to other subcutaneous tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: real-life data from the LORHEN registry.Int J Rheum Dis. 2018 Feb;21(2):422-430. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13199. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29082659
-
Optimizing biological treatment in rheumatoid arthritis with the aid of therapeutic drug monitoring.Dan Med J. 2016 Nov;63(11):B5311. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27808043 Review.
-
Do tumor necrosis factor inhibitors increase cancer risk in patients with chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disorders?Cytokine. 2018 Jan;101:78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.09.013. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 27688201 Review.
Cited by
-
Early prediction of clinical response to anti-TNF treatment using multi-omics and machine learning in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022 Apr 11;61(4):1680-1689. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab521. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022. PMID: 34175943 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay Between Systemic Inflammation, Myocardial Injury, and Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results From the LiiRA Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 May 7;13(9):e030387. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.030387. Epub 2024 Apr 30. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38686879 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Divergence of Cardiovascular Biomarkers of Lipids and Subclinical Myocardial Injury Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients With Increased Inflammation.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Jun;73(6):970-979. doi: 10.1002/art.41613. Epub 2021 May 9. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33615723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vasan R.S. Biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: molecular basis and practical considerations. Circulation. 2010;113:2335–2362. - PubMed
-
- Bluml S., Scheinecker C., Smolen J.S., Redlich K. Targeting TNF receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunol. 2012;24:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti S., Davidge S.T. Estradiol modulates tumor necrosis factor-induced endothelial inflammation: role of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2. J. Vasc. Res. 2013;50:21–34. - PubMed
-
- Doss G.P., Agoramoorthy G., Chakraborty C. TNF/TNFR: drug target for autoimmune diseases and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2014;19:1028–1040. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

