Effect of Si/Al ratio of high-silica HZSM-5 catalysts on the prins condensation of isobutylene and formaldehyde to isoprene
- PMID: 31193418
- PMCID: PMC6529679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01640
Effect of Si/Al ratio of high-silica HZSM-5 catalysts on the prins condensation of isobutylene and formaldehyde to isoprene
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Effect of Si/Al ratio of high-silica HZSM-5 catalysts on the prins condensation of isobutylene and formaldehyde to isoprene" [Heliyon 5 (5) (May 2019) e01640].Heliyon. 2019 Dec 5;5(12):e02889. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02889. eCollection 2019 Dec. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31872110 Free PMC article.
Abstract
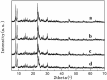
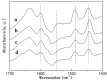
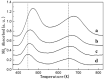
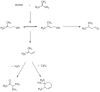
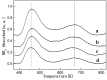
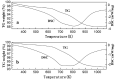
A series of HZSM-5 catalysts with different Si/Al ratio were prepared and characterized with various characteristic methods XRD, BET, NH3-TPD, FT-IR spectra of adsorbed pyridine, etc. The effect of Si/Al ratio of HZSM-5 catalysts on the prins condensation of isobutylene and formaldehyde to isoprene was investigated in detail. It is resulted that the catalytic activities are dependent on the acid strength, decreasing with the ratio of Si/Al increases. The optimized catalyst was HZSM-5 (600) with 8.8% of isobutene conversion and 90.2% of selectivity to isoprene, indicating that the higher Si/Al ratio was termed as appropriate for prins condensation of isobutylene and formaldehyde to isoprene. On the contrary, the low Si/Al ratio may lead to the formation of by-products and coke deposits, which leads the catalysts deactivation.
Keywords: Materials chemistry; Organic chemistry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corrigendum to "Effect of Si/Al ratio of high-silica HZSM-5 catalysts on the prins condensation of isobutylene and formaldehyde to isoprene" [Heliyon 5 (5) (May 2019) e01640].Heliyon. 2019 Dec 5;5(12):e02889. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02889. eCollection 2019 Dec. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31872110 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of metal doping on the coke formation of a novel hierarchical HZSM-5 zeolite catalyst in the conversion of 1-propanol to fuel blendstock.RSC Adv. 2025 Feb 6;15(6):3988-3999. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07707e. eCollection 2025 Feb 6. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39926233 Free PMC article.
-
Catalysis by coke deposits: synthesis of isoprene over solid catalysts.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 Dec 2;52(49):12961-4. doi: 10.1002/anie.201307083. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013. PMID: 24129943
-
Vapor-Phase Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid to γ-Valerolactone Over Bi-Functional Ni/HZSM-5 Catalyst.Front Chem. 2018 Jul 17;6:285. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00285. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 30065923 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol by supercritical CO2 in coordination with HZSM-5-catalyzed formaldehyde-isobutene Prins reaction.Turk J Chem. 2024 Jun 26;48(4):597-619. doi: 10.55730/1300-0527.3682. eCollection 2024. Turk J Chem. 2024. PMID: 39296791 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Upgrading furfural to bio-fuels using supported molybdenum carbides: study of the support effect.RSC Adv. 2024 Aug 27;14(37):26920-26932. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04256e. eCollection 2024 Aug 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39193305 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrolytic vs. Nonhydrolytic Sol-Gel in Preparation of Mixed Oxide Silica-Alumina Catalysts for Esterification.Molecules. 2022 Apr 14;27(8):2534. doi: 10.3390/molecules27082534. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35458732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taalman R.D.F.M. Isoprene: background and issues. Toxicology. 1996;113:242–246. - PubMed
-
- Dumitriu E., Hulea V., Chelaru C., Hulea T. Selective synthesis of isoprene by prins condensation using molecular sieves. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1994;84:1997–2004.
-
- Krzywicki A., Wilanowicz T., Malinowski S. Catalytic and physicochemical properties of the Al2O3-H3PO4 system, I. vapor phase condensation of isobutylene and formaldehyde the prins reaction. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 1979;11:399–403.
-
- Dumitriu E., Gongescu D., Hulea V. Contribution to the study of isobutene condensation with formaldehyde catalyzed by zeolites. Heterog. Catal. Fine Chem. III. 1993:669–676.
-
- Dang Z., Gu J., Yu L., Zhang C. Vapor-phase synthesis of isoprene from formaldehyde and isobutylene over CuSO4-MOx/SiO2 catalysts. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 1991;43:495–500.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

