Septic shock secondary to an acute necrotizing community-acquired pneumonia with bacteremia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 31193456
- PMCID: PMC6531848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00563
Septic shock secondary to an acute necrotizing community-acquired pneumonia with bacteremia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
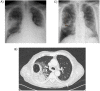
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an uncommon cause of necrotizing acute community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Only thirteen cases have been previously reported in the literature. In this article, we describe a case of previously healthy 80-year-old male patient, who presented in septic shock caused by necrotizing CAP. Despite inadequate empiric antimicrobial treatment, the patient survived and was able to return to his home after three weeks of hospitalization. To the best of our knowledge, this is the second case of septic shock secondary to P. aeruginosa necrotizing CAP and bacteremia, with optimal clinical outcome. We highlight the evolution of this pathology remains unpredictable, despite the factors related to the host and the bacterium.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; cavity lesion; community-acquired pneumonia; septic shock.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Young Healthy Patient With Severe COVID-19 and Fulminant Community-Acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia: A Case Report.Cureus. 2022 Dec 16;14(12):e32617. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32617. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36654604 Free PMC article.
-
Community-acquired necrotizing pneumonia with bacteremia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a patient with emphysema: An autopsy case report.Respir Investig. 2018 Mar;56(2):189-194. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2017.12.008. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Respir Investig. 2018. PMID: 29548659
-
Community-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa-pneumonia in a previously healthy man occupationally exposed to metalworking fluids.Autops Case Rep. 2014 Sep 30;4(3):31-37. doi: 10.4322/acr.2014.026. eCollection 2014 Jul-Sep. Autops Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 28573116 Free PMC article.
-
A case report of community-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia complicated with MODS in a previously healthy patient and related literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Feb 8;19(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-3765-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30736735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Septic shock due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a previously healthy woman.Intensive Care Med. 1995 Mar;21(3):226-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01701476. Intensive Care Med. 1995. PMID: 7790608 Review.
Cited by
-
A Fatal Case of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Community-Acquired Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Patient: Clinical and Molecular Characterization and Literature Review.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 24;11(5):1112. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051112. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination Therapy of Polymyxin B and Amikacin for Community-Acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia with MODS in a Previously Healthy Patient: A Case Report.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Jul 27;14:2895-2900. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S312601. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34349524 Free PMC article.
-
The Uncommon Suspect: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Cavitary Lung Lesions in an Immunocompetent Patient.Cureus. 2024 Aug 3;16(8):e66075. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66075. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39224733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kunimasa K., Ishida T., Kimura S. Successful Treatment of Community-Acquired fulminant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Necrotizing Pneumonia in a Previously Healthy Young Man. Intern Med. 2012;51(17):2473–2478. Epub 2012 Sep 1. - PubMed
-
- Crnich C.J., Gordon B., Andes D. Hot tub-associated necrotizing pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:e55–e57. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto N., Tsuchiya K., Hikone M. Community-acquired necrotizing pneumonia with bacteriemia Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a patient with emphysema: An autopsy case report. Respir Investig. 2018;56(Mar (2)):189–194. Epub 2018 Jan 12. - PubMed
-
- Vikram H.R., Shore E.T., Venkatesh P.R. Community Acquired Pneumonia Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Conn Med. 1999;63(May (5)):271–273. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

