The potential chemo preventive effect of ursolic acid isolated from Paulownia tomentosa, against N-diethylnitrosamine: initiated and promoted hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 31193530
- PMCID: PMC6536727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01769
The potential chemo preventive effect of ursolic acid isolated from Paulownia tomentosa, against N-diethylnitrosamine: initiated and promoted hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
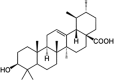
The present study discusses the isolation of ursolic acid from the chloroform extract of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb) Steud fruits and its cytotoxic effect has been assessed in-vitro was performed in different cells lines (A-549, MCF-7, HepG2) and in-vivo using N-diethylnitrosamine. The obtained results revealed that ursolic acid showed significant cytotoxic activity on MCF-7 and HepG2 cell lines in comparison to Doxorubicin as a reference drug. Moreover, we have assessed the inhibitory effects of Paulownia tomentosa fruit chloroform extract and the isolated ursolic acid on hepatocarcinogenesis was carried out for the first time using N-diethylnitrosamine, where the group treated with ursolic acid given orally after 8 weeks of cancer induction showed the most significant results in comparison to the chloroform extract. The effect of ursolic acid on intoxicated rats caused significant restoration of most of the normal hepatocytes architecture with regular dark nuclei and the group treated with Paulownia tomentosa fruits showed remarkable results with improvement in biochemical analysis.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Natural product chemistry; Pharmaceutical chemistry.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[Chemical Constituents of Paulownia tomentosa Fruits].Zhong Yao Cai. 2015 Mar;38(3):524-6. Zhong Yao Cai. 2015. PMID: 26495654 Chinese.
-
Phytochemical profile of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb). Steud.Phytochem Rev. 2015;14(5):799-833. doi: 10.1007/s11101-014-9376-y. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Phytochem Rev. 2015. PMID: 32214918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-geranylated flavonoids from Paulownia tomentosa Steud. fruit as potential anti-inflammatory agents.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 5;296:115509. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115509. Epub 2022 Jun 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35760257
-
[Studies on the chemical constituents from the leave of Paulownia tomentosa].Zhong Yao Cai. 2011 Feb;34(2):232-4. Zhong Yao Cai. 2011. PMID: 21823481 Chinese.
-
Paulownia Organs as Interesting New Sources of Bioactive Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 14;24(2):1676. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021676. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ursolic Acid-Based Derivatives as Potential Anti-Cancer Agents: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 18;21(16):5920. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165920. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32824664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral curative therapeutic study of N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced mouse liver damage of chitosan-coated ursolic acid niosomes.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 1;15(1):19225. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04571-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40451903 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the In Vitro Cytotoxic Activity of Ursolic Acid PLGA Nanoparticles against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines.Materials (Basel). 2021 Aug 29;14(17):4917. doi: 10.3390/ma14174917. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34501007 Free PMC article.
-
Plants-Derived Biomolecules as Potent Antiviral Phytomedicines: New Insights on Ethnobotanical Evidences against Coronaviruses.Plants (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;9(9):1244. doi: 10.3390/plants9091244. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ursolic acid: a natural modulator of signaling networks in different cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 10;22(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02804-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36496432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bansal A.K., Bansal M., Soni G., Bhavnagar D. Protective role of Vitamin E pre-treatment on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced oxidative stress in rat liver. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2005;156:3101–3111. - PubMed
-
- Valan M.F., John de britto A., Venkataraman R. Phytoconstituents with hepatoprotective activity. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2010;8(3):1421–1432.
-
- Kagawa M., Sano T., Ishibashi N., Hashimoto M., Okuno M., Moriwaki H. An acyclic retinoid, NIK-333, inhibits N-diethylnitrosamine-induced rat hepatocarcinogenesis through suppression of TGF-α expression and cell proliferation. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25(6):979–985. - PubMed
-
- Hamed M.A., Aly H.F., Ali S.A., Metwalley N.S., Hassan S.A., Ahmed S.A. In vitro and in vivo assessment of some functional foods against initiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012;2(1):471–483.
-
- Ali S.A., Ahmed S.A., Farrag A.H. Protective and prophylactic role of brassicaceae vegetables extracts on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced initiation of hepatocellular carcinoma in rat liver. Res. Rev.: Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicological Studies. 2015;1:1–19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

