Early life exposures, neurodevelopmental disorders, and transposable elements
- PMID: 31193573
- PMCID: PMC6536887
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2019.100174
Early life exposures, neurodevelopmental disorders, and transposable elements
Abstract
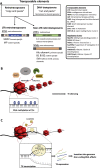
Transposable elements make up a much larger portion of the genome than protein-coding genes, yet we know relatively little about their function in the human genome. However, we are beginning to more fully understand their role in brain development, neuroinflammation, and adaptation to environmental insults such as stress. For instance, glucocorticoid receptor activation regulates transposable elements in the brain following acute stress. Early life is a period of substantial brain development during which transposable elements play a role. Environmental exposures and experiences during early life that promote abnormal regulation of transposable elements may lead to a cascade of events that ultimately increase susceptibility to disorders later in life. Recent attention to transposable elements in psychiatric illness has begun to clarify associations indicative of dysregulation of different classes of transposable elements in stress-related and neurodevelopmental illness. Though individual susceptibility or resiliency to psychiatric illness has not been explained by traditional genetic studies, the wide inter-individual variability in transposable element composition in the human genome make TEs attractive candidates to elucidate this differential susceptibility. In this review, we discuss evidence that regulation of transposable elements in the brain are stage-specific, sensitive to environmental factors, and may be impacted by early life perturbations. We further present evidence of associations with stress-related and neurodevelopmental psychiatric illness from a developmental perspective.
Keywords: Alu; Development; LINE1; Neurodevelopmental disorders; Retrotransposons; Stress.
Figures
References
-
- Agid O., Shapira B., Zislin J., Ritsner M., Hanin B., Murad H., Troudart T., Bloch M., Heresco-Levy U., Lerer B. Environment and vulnerability to major psychiatric illness: a case control study of early parental loss in major depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry. 1999;4:163–172. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . fifth ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; Arlington, VA: 2013. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

