The status of radiation oncology (RO) teaching to medical students in Europe
- PMID: 31193619
- PMCID: PMC6538841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2019.04.010
The status of radiation oncology (RO) teaching to medical students in Europe
Abstract
Aim: To provide an overview of Radiation Oncology (RO) teaching to medical students around Europe.
Materials and methods: An electronic survey was sent to European academic teachers of RO. The survey focused on the teaching of RO to medical students throughout their undergraduate education.
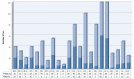
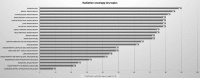
Results: A total of 87 academic RO teachers from 29 countries were invited to participate in the electronic survey. Thirty-two surveys were completed by respondents from 19 European countries (response rate: 37%). The median number of hours devoted to RO teaching was 10 h (mean 16 h, range 2-60). The number of hours assigned to RO teaching was equal or inferior compared to medical oncology. In two institutions (6%) RO was delivered as a stand-alone course with an individual knowledge assessment. In 30 institutions (94%), the RO course was taught and/or assessed in a modular curriculum with other disciplines. Radiobiology, breast, lung, gastrointestinal, gynecologic malignancies, RO adverse events and palliative RO were taught in 80% of institutions. Pediatric RO, RO for benign conditions and economic topics were taught in less than 30% of institutions. In most institutions, classical written and oral examinations were used. Computer-based examinations and/or objective structured clinical examinations (OSCE) were seldom used. E-learning methods were available in less than 10% of institutions. A clerkship in RO department was available in 28 out of 32 institutions (87%), less than 5% of medical students were involved in research in RO during their undergraduate education. Strategies to encourage medical students to consider RO as a future career were offered in 53% of institutions.
Conclusions: RO teaching to medical students was not uniform in Europe. RO teaching during undergraduate education in Europe was undervalued, and its knowledge and learning tools could be broadened and updated in the core curricula of medical students.
Keywords: Curriculum; Medical students; Radiation oncology; Undergraduate medical education.
Figures
References
-
- Steliarova-Foucher E., O’Callaghan M., Ferlay J., Masuyer E., Rosso S., Forman D. The European cancer observatory: a new data resource. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51:1131–1143. - PubMed
-
- Barton M.B., Jacob S., Shafiq J., Wong K., Thompson S.R., Hanna T.P. Estimating the demand for radiotherapy from the evidence: a review of changes from 2003 to 2012. Radiother Oncol. 2014;112:140–144. - PubMed
-
- Delaney G., Jacob S., Featherstone C., Barton M. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer. 2005;104:1129–1137. - PubMed
-
- Delaney G.P., Barton M.B. Evidence-based estimates of the demand for radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2015;27:70–76. - PubMed
-
- Cai B., Nickman N.A., Gaffney D.K. The cost-effectiveness of external beam radiation therapy in bone metastases. Curr Opin Supp Palliative Care. 2013;7:278–283. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

