Internet gaming disorder: Feeling the flow of social games
- PMID: 31193693
- PMCID: PMC6541905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abrep.2018.10.004
Internet gaming disorder: Feeling the flow of social games
Abstract
Introduction: Gaming Disorder (GD) was added to the recent publication of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) by the World Health Organization. This aligns with recommendations of the fifth edition of the Diagnostic Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5), issued by the American Psychiatric Association. Accordingly, further relevant research has been invited. The interplay between preference for online social game genres, the degree of online Flow (or immersive pleasure) experienced, and the gamer's biological gender were examined here as contributing factors of IGD.
Method: A normative sample of adult internet gamers was collected online (N = 237, Age = 18-59, Males = 157; 66%; Females = 80; 34%). Participants completed the nine-item Internet Gaming Disorder Scale-Short Form (IGDS-SF9), the Online Flow Questionnaire (OFQ), and also self-reported demographics and internet/gaming behaviours.
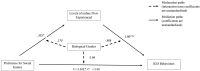
Results: Mediation and moderated mediation analyses indicated that the level of online Flow experienced considerably mediated the association between the preference for social games genres and the intensity of IGD behaviours across both biological genders.
Conclusions: Results suggest that the level of online Flow experienced constitutes a risk factor in relation to the development of IGD. Furthermore, games which mandate social interaction with others present to be conducive to online Flow, and thus enhancing IGD risk irrespective of the biological gender of the gamer. Implications and limitations of the study are discussed.
Keywords: Flow; Gaming addiction; Internet gaming disorder; Massively multiplayer online role playing games; Multiplayer online battle arena; Online flow; Social games.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measuring Female Gaming: Gamer Profile, Predictors, Prevalence, and Characteristics From Psychological and Gender Perspectives.Front Psychol. 2019 Apr 26;10:898. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00898. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31105622 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and Characterization of Online Substance Use Discussions Among Gamers: Qualitative Retrospective Analysis of Reddit r/StopGaming Data.JMIR Infodemiology. 2024 Oct 2;4:e58201. doi: 10.2196/58201. JMIR Infodemiology. 2024. PMID: 39357050 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary cross-cultural study of Hikikomori and Internet Gaming Disorder: The moderating effects of game-playing time and living with parents.Addict Behav Rep. 2018 Oct 26;9:001-1. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2018.10.001. eCollection 2019 Jun. Addict Behav Rep. 2018. PMID: 31193743 Free PMC article.
-
Internet Gaming Disorder: An Emergent Health Issue for Men.Am J Mens Health. 2018 Jul;12(4):1151-1159. doi: 10.1177/1557988318766950. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Am J Mens Health. 2018. PMID: 29606034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What We Know About Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games.Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2020 Mar/Apr;28(2):107-112. doi: 10.1097/HRP.0000000000000247. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32134835 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteus effect avatar profiles: Associations with disordered gaming and activity levels.Addict Behav Rep. 2024 Aug 2;20:100562. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2024.100562. eCollection 2024 Dec. Addict Behav Rep. 2024. PMID: 39219743 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Gaming Disorder, Self-Compensation Motivation, Game Flow, Time Spent Gaming, and Fear of Missing Out Among a Sample of Chinese University Students: A Network Analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Nov 1;12:761519. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.761519. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34790137 Free PMC article.
-
From game engagement to craving responses - The role of gratification and compensation experiences during video-gaming in casual and at-risk gamers.Addict Behav Rep. 2023 Nov 30;18:100520. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2023.100520. eCollection 2023 Dec. Addict Behav Rep. 2023. PMID: 38149224 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with smartphone addiction among nursing postgraduates during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multilevel study from China's mainland.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Dec 6;23(1):915. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05369-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38057732 Free PMC article.
-
Internet gaming disorder behaviours: a preliminary exploration of individualism and collectivism profiles.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 May 20;21(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03245-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34016087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abuhamdeh S., Csikszentmihalyi M. The importance of challenge for the enjoyment of intrinsically motivated, goal-directed activities. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. 2012;38(3):317–330. - PubMed
-
- Adams B.L., Stavropoulos V., Burleigh T.L., Liew L.W., Beard C.L., Griffiths M.D. Internet gaming disorder behaviors in emergent adulthood: A pilot study examining the interplay between anxiety and family cohesion. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. 2018:1–17.
-
- Agmon M., Perry C.K., Phelan E., Demiris G., Nguyen H.Q. A pilot study of Wii Fit exergames to improve balance in older adults. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy. 2011;34(4):161–167. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi K., Saghafi A. Psychosocial profile of Iranian adolescents' Internet addiction. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking. 2013;16(7):543–548. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; Arlington, VA: 2013. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources