Modeling improved production of the chemotherapeutic polypeptide actinomycin D by a novel Streptomyces sp. strain from a Saharan soil
- PMID: 31193702
- PMCID: PMC6538969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01695
Modeling improved production of the chemotherapeutic polypeptide actinomycin D by a novel Streptomyces sp. strain from a Saharan soil
Abstract
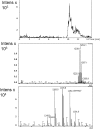
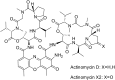
The novel bioactive actinobacterial strain GSBNT10 obtained from a Saharan soil, was taxonomically characterized using a polyphasic approach. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis supported the classification of the isolate within the genus Streptomyces indicating it as a novel species. The major metabolite responsible of the bioactivity was purified and structurally characterized as actinomycin D (act-D) by mass spectrometric and nuclear magnetic resonance analyses Plackett-Burman design (PBD) and response surface methodology (RSM) were applied in order to optimize the medium formulation for the production of this bioactive metabolite. By PBD experiments, NaNO3, K2HPO4 and initial pH value were selected as significant variables affecting the metabolite production. Central Composite Design (CCD) showed that adjustment of the fermentative medium at pH 8.25, K2HPO4 at 0.2 gL-1 and NaNO3 at 3.76 gL-1 were the values suiting the production of act-D. Moreover, the results obtained by the statistical approach were confirmed by act-D detection using the HPLC equipped with a diode array detector and coupled online with electrospray-mass spectrometry (ESIMS) technique. act-D production was highly stimulated, obtaining a good yield (656.46 mgL-1) which corresponds to a 58.56% increase compared with the non-optimized conditions and data from LC-ESIMS technique efficiently confirmed the forecast from RSM.
Keywords: Actinomycin D; Central composite design; Electrospray mass spectrometry; Microbiology; Optimization; Plackett-Burman design; Saharan saline soil; Streptomyces sp..
Figures




Similar articles
-
Streptomyces thermoviolaceus SRC3 strain as a novel source of the antibiotic adjuvant streptazolin: A statistical approach toward the optimized production.J Microbiol Methods. 2018 May;148:161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2018.04.008. Epub 2018 Apr 14. J Microbiol Methods. 2018. PMID: 29665368
-
Improved antimicrobial compound production by a new isolate Streptomyces hygroscopicus MTCC 4003 using Plackett-Burman design and response Surface methodology.Bioinformation. 2012;8(21):1021-5. doi: 10.6026/97320630081021. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Bioinformation. 2012. PMID: 23275700 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of saltern based Streptomyces sp. and statistical media optimization for its improved antibacterial activity.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jan 21;5:753. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00753. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25653640 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling-based optimization approaches for the development of Anti-Agrobacterium tumefaciens activity using Streptomyces sp TN71.Microb Pathog. 2018 Jun;119:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.04.006. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29626659
-
Optimization of fermentation conditions through response surface methodology for enhanced antibacterial metabolite production by Streptomyces sp. 1-14 from cassava rhizosphere.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 14;13(11):e0206497. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206497. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30427885 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Profile of Actinomycin D Analogs Secreted by Egyptian Desert Streptomyces sp. DH7.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Oct 18;10(10):1264. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10101264. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680844 Free PMC article.
-
Actinobacteria Derived from Algerian Ecosystems as a Prominent Source of Antimicrobial Molecules.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Oct 1;8(4):172. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8040172. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31581466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of Antibacterial Activity of Paludifilum halophilum and Identification of N-(1-Carboxy-ethyl)-phthalamic Acid as the Main Bioactive Compound.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Feb 12;2020:4805706. doi: 10.1155/2020/4805706. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32104693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avendaño C., Menéndez J.C. Anticancer drugs acting via radical species, photosensitizers and photodynamic therapy of cancer. In: Avendaño C., Menéndez J.C., editors. Medicinal Chemistry of Anticancer Drugs. first ed. Elsevier Science; Linacre House, Jordan Hill, Oxford, OX2 8DP, UK: 2008. pp. 93–138.
-
- Chaabane Chaouch F., Bouras N., Mokrane S., Zitouni A., Schumann P., Spröer C., Sabaou N., Klenk H.P. Streptosporangium becharense sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from desert soil. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 2016;66:2484–2490. - PubMed
-
- Chen C., Wang Q., Song F., Abdel-Mageed W.M., Guo H., Fu C., Hou W., Dai H., Liu X., Yang N., Xie F., Yu K., Chen R., Zhang L. A marine-derived Streptomyces sp. MS449 produces high yield of actinomycin X2 and actinomycin D with potent anti-tuberculosis activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012;95:919–927. - PubMed
-
- Dalili M., Chau P.C. Production of Actinomycin-D with immobilized Streptomyces parvulus under nitrogen and carbon starvation conditions. Biotechnol. Lett. 1988;10:331–336.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

