Learning functions in short-term cocaine users
- PMID: 31193767
- PMCID: PMC6542742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abrep.2019.100169
Learning functions in short-term cocaine users
Abstract
Objective: This study examined learning functions in short-term cocaine users and control participants.
Method: Seventeen active cocaine users (reporting 3.5 mean years of cocaine use) and seventeen non-cocaine-using controls (with similar reported levels of alcohol and marijuana use) were compared on tasks measuring different aspects of learning.
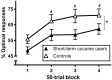
Results: The cocaine users performed more poorly on the Weather Prediction and List-Learning tasks, as well as supplementary executive and psychomotor function tasks, than controls.
Conclusions: Individuals with a relatively short duration of cocaine use exhibited moderate weaknesses in probabilistic category learning, verbal learning and psychomotor functions, relative to controls. These weaknesses may underpin difficulty in learning from the probabilistic consequences of behavior and hinder the ability to respond to cognitive-behavioral treatments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A decrement in probabilistic category learning in cocaine users after controlling for marijuana and alcohol use.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014 Feb;22(1):65-74. doi: 10.1037/a0034506. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24188172
-
Stimulus-response learning in long-term cocaine users: acquired equivalence and probabilistic category learning.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008 Jan 11;93(1-2):155-62. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.09.013. Epub 2007 Oct 31. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008. PMID: 17976927 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive function in aging cocaine smokers.J Psychopharmacol. 2019 Jul;33(7):801-810. doi: 10.1177/0269881119849812. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31169441
-
Drug-related decrease in neuropsychological functions of abstinent drug users.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2011 Mar;4(1):42-56. doi: 10.2174/1874473711104010042. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2011. PMID: 21466500 Review.
-
Cognitive consequences of cannabis use: comparison with abuse of stimulants and heroin with regard to attention, memory and executive functions.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005 Jun;81(2):319-30. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2005.02.017. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005. PMID: 15925403 Review.
Cited by
-
Mixed amphetamine salts-extended release (MAS-ER) as a behavioral treatment augmentation strategy for cocaine use disorder: A randomized clinical trial.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2024 Feb;32(1):112-127. doi: 10.1037/pha0000676. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37732961 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dopamine receptor antagonists effects on low-dimensional attractors of local field potentials in optogenetic mice.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 16;14(10):e0223469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223469. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31618234 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent-onset vs. adult-onset cocaine use: Impact on cognitive functioning in animal models and opportunities for translation.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Sep;196:172994. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172994. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 32659242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated cocaine exposure prior to fear conditioning induces persistency of PTSD-like symptoms and enhancement of hippocampal and amygdala cell density in male rats.Brain Struct Funct. 2021 Sep;226(7):2219-2241. doi: 10.1007/s00429-021-02320-w. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Brain Struct Funct. 2021. PMID: 34195855
-
Cocaine Administration and Its Abstinence Conditions Modulate Neuroglia.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 27;21(21):7970. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217970. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33120991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aharonovich E., Hasin D.S., Nunes E.V., Stohl M., Cannizzaro D., Sarvet A.…Genece K.G. Modified cognitive behavioral therapy (M-CBT) for cocaine dependence: Development of treatment for cognitively impaired users and results from a Stage 1 trial. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors. 2018;32(7):800–811. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Chiara G. Drug addiction as dopamine-dependent associative learning disorder. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1999;375(1–3):13–30. - PubMed
-
- Frazer K.M., Richards Q., Keith D.R. The long-term effects of cocaine use on cognitive functioning: A systematic critical review. Behavioural Brain Research. 2018;348:241–262. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources