Need fulfilment and internet gaming disorder: A preliminary integrative model
- PMID: 31193898
- PMCID: PMC6543453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abrep.2018.100144
Need fulfilment and internet gaming disorder: A preliminary integrative model
Abstract
Background: The need for a better understanding of the risk factors underpinning disordered gaming has been consistently emphasized. Although, gaming may offer a simple and straightforward means of alleviating distress, relying on gaming to address one's unmet psychological needs could invite problematic usage. Self-determination theory highlights the significance of three universally inherent psychological needs for relatedness, competency, and autonomy. A motivation to engage in gaming may be to address unmet needs and may become problematic.
Objective: This study aimed to assess whether experienced levels of loneliness, depression and self-esteem mediate the association between Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) behaviours and Need-Fulfilment deficits.
Method: The participants comprised of 149 adults (83 males, 66 females), aged between 18 and 62 years. A series of self-reported questionaries assessing their levels of IGD behaviours, depression, loneliness, self-esteem and need-fulfilment were completed.
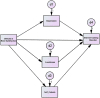
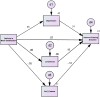
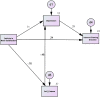
Results: Need-fulfilment deficits were linked to higher IGD behaviours. Interestingly, this association was mediated by the reported levels of self-esteem and depression and not loneliness.
Conclusions: The findings lend further empirical support for the mediating role of psychological distress between need fulfilment deficits and IGD behaviours.
Keywords: Internet gaming disorder; Need-fulfilment; Psychological distress; Self-determination.
Figures
References
-
- Adams B.L., Stavropoulos V., Burleigh T.L., Liew L.W., Beard C.L., Griffiths M.D. Internet gaming disorder behaviors in emergent adulthood: A pilot study examining the interplay between anxiety and family cohesion. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. 2018:1–17.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . 5th ed. Author; Washington, DC: 2013. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders.
-
- Anderson E.L., Steen E., Stavropoulos V. Internet use and problematic internet use: A systematic review of longitudinal research trends in adolescence and emergent adulthood. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth. 2017;22:430–454.
-
- Ballabio M., Griffiths M.D., Urbán R., Quartiroli A., Demetrovics Z., Király O. Do gaming motives mediate between psychiatric symptoms and problematic gaming? An empirical survey study. Addiction Research & Theory. 2017;25(5):397–408.
-
- Baron R.M., Kenny D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;51.6:1173. 0022-3514/86/S00.75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources