AMF siRNA treatment of keloid through inhibition signaling pathway of RhoA/ROCK1
- PMID: 31193978
- PMCID: PMC6545443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2018.05.002
AMF siRNA treatment of keloid through inhibition signaling pathway of RhoA/ROCK1
Abstract
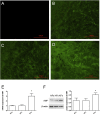
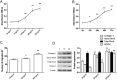
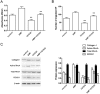
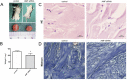
A keloid (KD) is a benign dermal fibrotic tumor. Treatment of KDs is challenging and the recurrence rate is high; thus, there is an unmet need to explore new target sites and new treatment methods. As a tumor-associated cytokine, autocrine motility factor (AMF) can effectively stimulate the random and directional movement of cells. We first found that AMF was overexpressed in keloid fibroblasts (KFs) and the proliferation and migration of KFs were promoted by AMF stimulation. After treatment with Y-27632, RhoA kinase inhibitor, the proliferation and migration capacity of KFs declined significantly, and type I collagen protein, active RhoA and ROCK1 also were downregulated. In addition, a KD transplantation model was established under the skin of nude mice, with KD intramural injection AMF siRNA, we found that the weight of the KD was smaller than in the control group (P < 0.05), KD tissue sections stained by HE and Masson showed that fibers became loose and the blood vessels were visibly reduced. In conclusion, AMF siRNA is expected to be a novel strategy to treat KD by inhibiting signaling pathway of RhoA/ROCK1.
Keywords: Autocrine motility factor; Keloid; RhoA; SIRNA; Treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses collagen production and proliferation in keloid fibroblasts via inhibition of the STAT3-signaling pathway.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Oct;128(10):2429-41. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.103. Epub 2008 May 8. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18463684
-
Activation of small GTPase Rho is required for autocrine motility factor signaling.Cancer Res. 2002 Aug 1;62(15):4484-90. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12154059
-
miR-188-5p regulates proliferation and invasion via PI3K/Akt/MMP-2/9 signaling in keloids.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019 Feb 1;51(2):185-196. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmy165. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019. PMID: 30668826
-
Silencing NLRC5 inhibits extracellular matrix expression in keloid fibroblasts via inhibition of transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:1016-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.08.012. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27525969
-
Novel roles of the autocrine motility factor/phosphoglucose isomerase in tumor malignancy.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004 Dec;11(4):749-59. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00811. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15613449 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-21 may be involved in the therapeutic effects of Galla chinensis ointment on keloid.J Int Med Res. 2020 Mar;48(3):300060520909602. doi: 10.1177/0300060520909602. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32216491 Free PMC article.
-
Keloid Disorder: Genetic Basis, Gene Expression Profiles, and Immunological Modulation of the Fibrotic Processes in the Skin.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2023 Jul 5;15(7):a041245. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041245. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2023. PMID: 36411063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALKBH5 Inhibits YTHDF2-m6A-Mediated Degradation of RCN1 mRNA to Promote Keloid Formation by Activating IRE1α-XBP1-Mediated ER Stress.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Apr;24(4):e70177. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70177. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40214031 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of keloids through Runx2 siRNA‑induced inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):55. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11693. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33200804 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Insights into Keloid Pathogenesis and Advanced Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 12;25(16):8776. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168776. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tuan T.L., Zhu J.Y., Sun B. Elevated levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 may account for the altered fibrinolysis by keloid fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106(5):1007–1011. - PubMed
-
- Slemp A.E., Kirschner R.E. Keloids and scars: a review of keloids and scars, their pathogenesis, risk factors, and management. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2006;18(4):396–402. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa R. Keloids as a serious disease such as malignancy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;122(3):993–994. - PubMed
-
- Yao X., Cui X., Wu X. Tumor suppressive role of miR-1224-5p in keloid proliferation, apoptosis and invasion via the TGF-beta 1/Smad 3 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(1):713–720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

