Protective activity of geraniol against acetic acid and Helicobacter pylori- induced gastric ulcers in rats
- PMID: 31193983
- PMCID: PMC6544613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2018.05.001
Protective activity of geraniol against acetic acid and Helicobacter pylori- induced gastric ulcers in rats
Abstract
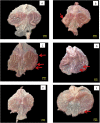
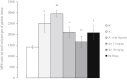
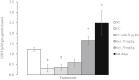
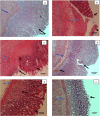
Geraniol, an active constituent of rose and palmarosa essential oils, possesses several pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, antibacterial and antiulcer activity. Geraniol was therefore investigated for its antiulcer and anti-Helicobacter pylori activity in rats. Ulcers were induced by injecting acetic acid into the sub-serosal layer of the stomach followed by orogastric inoculation of H. pylori for 7 days. Geraniol (15 and 30 mg/kg), vehicle and a standard drug combination (amoxicillin, 50 mg/kg; clarithromycin, 25 mg/kg and omeprazole, 20 mg/kg) were administered twice daily for 14 days. All the parameters were measured at the end of treatment. The ulcer index was significantly (P < 0.05) lowered in geraniol and standard drug-treated rats as compared to the H. pylori control group (4.13 ± 0.43). Treatment with geraniol (30 mg/kg) significantly (P < 0.01) increased the gastric pH along with a reduction in total acidity and gastric juice volume. Geraniol significantly (P < 0.05) attenuated the myeloperoxidase activity and augmented the total glutathione level in gastric mucosa. The extent of damage in the stomach was measured using a histopathological score. The score in H. pylori control, geraniol (30 mg/kg) and standard drugs was 9, 3.5 and 2.0 respectively. In the rapid urease test, treatment with geraniol (30 mg/kg) and the standard drugs produced a 33% and 67% cure respectively from H. pylori infection. Further, the reduction in bacterial load in the gastric mucosa was confirmed using modified Giemsa staining. Geraniol was observed to exhibit significant antiulcer and anti-H. pylori activity in a rodent model.
Keywords: Antiulcer; Geraniol; Glutathione; Helicobacter pylori; Myeloperoxidase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cochlospermum regium (Mart. ex Schrank) Pilg.: Evaluation of chemical profile, gastroprotective activity and mechanism of action of hydroethanolic extract of its xylopodium in acute and chronic experimental models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Apr 6;233:101-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30611907
-
Evidence of gastric ulcer healing activity of Maytenus robusta Reissek: In vitro and in vivo studies.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 4;175:75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26364940
-
Healing of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric ulcers in Mongolian gerbils: combined treatment with omeprazole and clarithromycin.Dig Dis Sci. 1999 Feb;44(2):257-65. doi: 10.1023/a:1026685929992. Dig Dis Sci. 1999. PMID: 10063909
-
[Pharmacological study on the pathological changes of the gastric mucosa in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Oct;118(4):259-68. doi: 10.1254/fpj.118.259. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11680169 Review. Japanese.
-
Clarithromycin and omeprazole as helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in patients with H. pylori-associated gastric disorders.Drugs. 1996 Jan;51(1):161-78. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199651010-00010. Drugs. 1996. PMID: 8741237 Review.
Cited by
-
AdipoRon, an Orally Active, Synthetic Agonist of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 Receptors Has Gastroprotective Effect in Experimentally Induced Gastric Ulcers in Mice.Molecules. 2021 May 15;26(10):2946. doi: 10.3390/molecules26102946. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34063466 Free PMC article.
-
The implication of the crosstalk of Nrf2 with NOXs, and HMGB1 in ethanol-induced gastric ulcer: Potential protective effect is afforded by Raspberry Ketone.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 12;14(8):e0220548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220548. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31404064 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of antioxidant and anti-ulcerogenic effects of Eremurus persicus (Jaub & Spach) Boiss leaf hydroalcoholic extract on ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Oct;29(5):1503-1518. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00868-x. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34435283
-
One Hundred Faces of Geraniol.Molecules. 2020 Jul 21;25(14):3303. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143303. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32708169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of snakehead fish extract supplementation to first-line eradication regimen on macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) expression in rats induced by Helicobacter pylori infection.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2020 May 8;7(2):209-217. doi: 10.5455/javar.2020.g411. eCollection 2020 Jun. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2020. PMID: 32607351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klopell F.C., Lemos M., Sousa J.P.B. Nerolidol, an antiulcer constituent from the essential oil of Baccharis dracunculifolia DC (Asteraceae) Z Naturforsch C Biosci. 2007;62(7–8):537–542. - PubMed
-
- Lima Z.P., Severi J.A., Pellizzon C.H. Can the aqueous decoction of mango flowers be used as antiulcer agent? J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;106:29–37. - PubMed
-
- Barros M.P., Lemos M., Maistro E.L. Evaluation of antiulcer activity of the main phenolic acids found in Brazilian Green Propolis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;120:372–377. - PubMed
-
- Belaiche J., Burette A., De Vos M., Louis E., Huybrechts M., Deltenre M. Observational survey of NSAID-related upper gastro-intestinal adverse events in Belgium. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2002;65:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Ej K., Jc T., Hp F. The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1994;9(Suppl. 2):59–69. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
