Methanol extract of Cola nitida ameliorates inflammation and nociception in experimental animals
- PMID: 31194116
- PMCID: PMC6550122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2019.100027
Methanol extract of Cola nitida ameliorates inflammation and nociception in experimental animals
Abstract
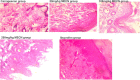
Methanol extract of Cola nitida (MECN) was evaluated for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities using rats and mice. Inflammatory activity of MECN was assessed by carrageenan-induced paw oedema while analgesic activity was evaluated by acetic acid -induced writhing and formalin paw lick test. Histological analyses of the paws were also carried out. There was evaluation of the mechanism(s) of action of MECN using naloxone, a blocker of opioid receptors; atropine, blocker of muscarinic receptors; and propranolol, blocker of beta adrenergic receptors. Findings from the study revealed that MECN has both anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. These properties were found to be dose dependent with 200 mg/kg of MECN discovered to be the most potent dose. 200 mg/kg was able to cause statistically significant reduction in paw size (p < 0.001) when compared with the carrageenan group. Histological analysis revealed that rats treated with 200 mg/kg of MECN showed no inflammatory cells in the left paw compared to other groups treated with carrageenan. In the formalin test, the number of paw licking was significantly reduced by MECN at 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg in both neurogenic and inflammatory pain responses (p < 0.001) even as 200 mg/kg showed the highest percentage inhibition of 98.17% while 100 mg/kg of aspirin showed percentage inhibition of 93.66%. In acetic acid-induced writhing test, 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg of MECN produced significant inhibition of writhes when compared with control as highest inhibition is observed in mice that received 200 mg/kg which is similar to aspirin. Administration of propranolol and naloxone was unable to reverse the analgesic function of MECN. However, atropine administration blocked the analgesic function of MECN. This shows that MECN exhibits its analgesic property through cholinergic pathway and not opioid and adrenergic pathways. Phytochemical screening revealed that MECN contains flavonoids, steroids, saponins, tannins, anthraquinines, terpenoids, and alkanoids. These phytochemical contents may thus be responsible for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Keywords: Analgesic; Anti-inflammation; Carrageenan; Cola nitida.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities of grapevine leaf extract (Vitis vinifera) in mice and identification of its active constituents by LC-MS/MS analyses.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:1088-1098. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.033. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27780137
-
Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties of the ethanolic extract of Lagenaria breviflora whole fruit in rat and mice.Niger J Physiol Sci. 2011 Nov 28;26(1):71-6. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22314991
-
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of 80% methanol root extract of Jasminum abyssinicum Hochst. ex. Dc. (Oleaceae) in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Apr 18;202:281-289. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.036. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28242384
-
Evaluation of the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, phytochemical and toxicological properties of the methanolic leaf extract of commercially processed Moringa oleifera in some laboratory animals.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;26(5):491-9. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2014-0105. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26020553
-
Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects of methanol extract from Bauhinia racemosa stem bark in animal models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Apr 26;98(3):267-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.01.018. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15814258 Review.
Cited by
-
Indigenous Nigeria medicinal herbal remedies: A potential source for therapeutic against rheumatoid arthritis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Jul;247(13):1148-1178. doi: 10.1177/15353702221102901. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35708153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the possible mechanism involved in the anti-nociceptive effect of β-sitosterol: modulation of oxidative stress, nitric oxide and IL-6.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Feb;31(1):517-527. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01122-8. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36574096
References
-
- Adedayo L.D., Olawuyi D.A., Ojo A.O., Bamidele O., Onasanwo S.A., Ayoka A.O. The role of aripriprazole (an anti-psychotic drug) in the resolution of acute peripheral inflammation in male wistar rats. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2017;17(6):1–8.
-
- Adesanwo J.K., Ogundele S.B., Akinpelu D.A., McDonald A.G. Chemical analyses, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of extracts from Cola nitida seed. J. Explor. Res. Pharmacol. 2017;2(3):67–77.
-
- Adisa W.A., Otamere H.O., Osifo C.U., Idonije O.B., Nwoke E.O. Effects of aqueous extract of kola nut (Cola nitida Rubra) on reproductive hormones in rats. Nig. J. Physiol. Sci. 2010;25:121–123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

