A Comparative Health Utility Value Analysis of Outcomes for Patients Following Septorhinoplasty With Previous Nasal Surgery
- PMID: 31194223
- PMCID: PMC6567843
- DOI: 10.1001/jamafacial.2019.0176
A Comparative Health Utility Value Analysis of Outcomes for Patients Following Septorhinoplasty With Previous Nasal Surgery
Abstract
Importance: Using health utility values (HUVs) as an outcome measure for surgical procedures, including rhinoplasty, allows for a standardized measurement of the qualitative and financial benefit of that procedure on overall health.
Objective: To use Euroqol 5-Dimension (EQ-5D)-derived HUVs to evaluate nasal obstruction outcomes following surgery between primary rhinoplasty (PSRP) and rhinoplasty with previous nasal surgery (RNS) in a prospective cohort study.
Design, setting, and participants: A single-institution prospective cohort study between 2013 and 2017 was carried out including 185 patients who underwent RNS before functional rhinoplasty and 278 patients who underwent PSRP for nasal obstruction. The analysis was carried out between December 2018 and February 2019.
Main outcomes and measures: Patients in the RNS cohort and PSRP cohort who completed the EQ-5D questionnaire immediately prior to surgery and postoperatively at 2, 4, 6, and 12 months were included in the study. The EQ-5D scores were converted to HUV scores and compared to evaluate for improvement in health status following surgery.
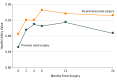
Results: Of the 185 patients in the RNS cohort, 97 (52%) were women and the mean (SD) age was 42.6 (13.4) years. Of the 278 in the PSRP cohort, 156 (55%) were women and the mean (SD) age was 36.0 (15.8) years. Both cohorts experienced significant improvement in HUV postoperatively. The mean (SD) HUV values were decreased in the RNS cohort versus the PSRP cohort both preoperatively (0.85 [0.16] versus 0.89 [0.14]) and postoperatively at 1 year (0.92 [0.14] versus 0.94 [0.11]); however, the difference in HUV was not statistically significant after 6 months postoperatively. Patients in the RNS cohort were typically older (76 [41%] older than 40 years vs 84 [31%], P = .02) and more likely to have sleep apnea (31 [19%] vs 24 [10%], P = .01) than in the PSRP cohort. On multivariable analysis, the use of spreader grafts and alar rim grafts in the PSRP cohort was significantly associated with improved HUV at 12 months. (r = -0.06; 95% CI, -0.11 to -0.01, P = .03).
Conclusions and relevance: Patients with a history of prior nasal surgery may represent a unique cohort when assessing health utility outcomes. Euroqol 5-dimension questionnaire-derived HUVs are a valid predictor of outcomes in all patients who undergo septorhinoplasty. Although outcomes were significantly improved for both cohorts, previous surgical history should be considered when performing cost utility analysis on the benefits of functional rhinoplasty.
Level of evidence: 3.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health Utility Values as an Outcome Measure in Patients Undergoing Functional Septorhinoplasty.JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2019 Sep 1;21(5):381-386. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2019.0234. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 31120515 Free PMC article.
-
Health Impairment From Nasal Airway Obstruction and Changes in Health Utility Values From Septorhinoplasty.JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2019 Mar 1;21(2):146-151. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2018.1368. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 30452512 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the EuroQol 5-Dimension Questionnaire for Detection of Clinically Significant Global Health-Related Quality-of-Life Improvement Following Functional Septorhinoplasty.JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2017 Mar 1;19(2):95-100. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2016.1410. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2017. PMID: 27893020
-
Rhinoplasty and septorhinoplasty outcome evaluation.Ear Nose Throat J. 2012 Mar;91(3):E10-4. doi: 10.1177/014556131209100315. Ear Nose Throat J. 2012. PMID: 22430341 Review.
-
"Should Pediatric Septal Surgery and Septorhinoplasty Be Performed for Nasal Obstruction?"-A Systematic Review of the Literature.Facial Plast Surg. 2024 Jun;40(3):378-393. doi: 10.1055/a-2219-9266. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Facial Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38035612
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Health State Utility Values in the Plastic Surgery Literature.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Nov 29;9(11):e3944. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003944. eCollection 2021 Nov. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 34849317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cherry DK, Woodwell DA, Rechtsteiner EA. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2005 summary. Adv Data. 2007;(387):1-39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
