Risk of spontaneous preterm birth and fetal growth associates with fetal SLIT2
- PMID: 31194736
- PMCID: PMC6563950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008107
Risk of spontaneous preterm birth and fetal growth associates with fetal SLIT2
Abstract
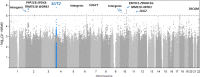
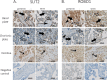
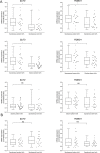
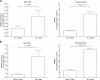
Spontaneous preterm birth (SPTB) is the leading cause of neonatal death and morbidity worldwide. Both maternal and fetal genetic factors likely contribute to SPTB. We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) on a population of Finnish origin that included 247 infants with SPTB (gestational age [GA] < 36 weeks) and 419 term controls (GA 38-41 weeks). The strongest signal came within the gene encoding slit guidance ligand 2 (SLIT2; rs116461311, minor allele frequency 0.05, p = 1.6×10-6). Pathway analysis revealed the top-ranking pathway was axon guidance, which includes SLIT2. In 172 very preterm-born infants (GA <32 weeks), rs116461311 was clearly overrepresented (odds ratio 4.06, p = 1.55×10-7). SLIT2 variants were associated with SPTB in another European population that comprised 260 very preterm infants and 9,630 controls. To gain functional insight, we used immunohistochemistry to visualize SLIT2 and its receptor ROBO1 in placentas from spontaneous preterm and term births. Both SLIT2 and ROBO1 were located in villous and decidual trophoblasts of embryonic origin. Based on qRT-PCR, the mRNA levels of SLIT2 and ROBO1 were higher in the basal plate of SPTB placentas compared to those from term or elective preterm deliveries. In addition, in spontaneous term and preterm births, placental SLIT2 expression was correlated with variations in fetal growth. Knockdown of ROBO1 in trophoblast-derived HTR8/SVneo cells by siRNA indicated that it regulate expression of several pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein (PSG) genes and genes involved in inflammation. Our results show that the fetal SLIT2 variant and both SLIT2 and ROBO1 expression in placenta and trophoblast cells may be correlated with susceptibility to SPTB. SLIT2-ROBO1 signaling was linked with regulation of genes involved in inflammation, PSG genes, decidualization and fetal growth. We propose that this receptor-ligand couple is a component of the signaling network that promotes SPTB.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations in Gene Coding for SLIT2 Linked to Preterm Birth: SLIT2 and its receptor ROBO1 are components of the signaling network that promotes spontaneous preterm birth.Am J Med Genet A. 2019 Sep;179(9):1684-1685. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.40459. Am J Med Genet A. 2019. PMID: 31393085 No abstract available.
-
Alterted SLIT2/ROBO1 signalling is linked to impaired placentation of missed and threatened miscarriage in early pregnancy.Histopathology. 2017 Oct;71(4):543-552. doi: 10.1111/his.13250. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Histopathology. 2017. PMID: 28485101
-
CXCR3 Polymorphism and Expression Associate with Spontaneous Preterm Birth.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):2187-98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501174. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26209629
-
Slit2/Robo1 signaling in glioma migration and invasion.Neurosci Bull. 2010 Dec;26(6):474-8. doi: 10.1007/s12264-010-0730-9. Neurosci Bull. 2010. PMID: 21113198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spontaneous preterm birth: advances toward the discovery of genetic predisposition.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Mar;218(3):294-314.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29248470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of microRNAs in trophoblast invasion and spiral artery remodeling: Implications for preeclampsia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 3;10:995462. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.995462. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36263015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Equitable Representation of Race, Ethnicity, and Ancestry Among Genomic Studies of Preterm Birth: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Feb 7;16(2):e53757. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53757. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38465134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extravillous trophoblast migration and invasion: Impact of environmental chemicals and pharmaceuticals.Reprod Toxicol. 2022 Jan;107:60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.11.008. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Reprod Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34838982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling the genetic landscape of cervical insufficiency: Insights into connective tissue dysfunction and hormonal pathways.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 19;19(9):e0310718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310718. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39298385 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated human placental heat shock protein 5 is associated with spontaneous preterm birth.Pediatr Res. 2023 Aug;94(2):520-529. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02501-9. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 36788289 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

