Is there any association between Toxoplasma gondii infection and depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31194852
- PMCID: PMC6564815
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218524
Is there any association between Toxoplasma gondii infection and depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) is an obligate intracellular opportunistic parasite that is the causative agent of toxoplasmosis. This parasite accounts for mental disorders; however, the relationship between T. gondii infection and depressive disorder is unclear. Regarding this, the present systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted to investigate the scientific evidence regarding the potential association between major depression disorder (MDD) and Toxoplasma infection.
Methods: For the purpose of the study, the articles related to the subject of interest were systematically searched in seven electronic databases. Special attention was given to the studies examining T. gondii seropositivity level in depressed patients and controls.
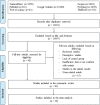
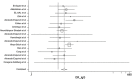
Results: The search process resulted in the identification of a total of 30 publications meeting the inclusion criteria and published up to April 2018 for the systematic review. Furthermore, 29 studies met the inclusion criteria to be entered into meta-analysis. Our meta-analysis involved the review of cross-sectional studies including 1657 depressed patients and 19565 individuals as controls and case-control studies entailing 1311 depressed cases and 6015 controls without depression. 1582 depressed people participated in cross-sectional studies whose results were reported as odds ratio (OR). In addition, the total number of participants was 15068 in this type of studies. Statistical analysis indicated that the pooled OR of the risk of anti-T. gondii IgG antibody in depressed individuals in case-control and cross-sectional studies was 1.15 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.95-1.39).
Conclusions: As the findings of the reviewed articles indicated, toxoplasmosis is not a risk factor for MDD. However, it is necessary to perform further research to clarify the detailed association between T. gondii and dysthymia or mild and moderate depression. Furthermore, it is recommended to better investigate the effect of antibody titers on the relationship between depression and T. gondii infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma gondii infection and risk of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathog Glob Health. 2020 May;114(3):117-126. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2020.1738153. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Pathog Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32186992 Free PMC article.
-
The global seroprevalence of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in women who had spontaneous abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Mar 13;14(3):e0008103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008103. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32168351 Free PMC article.
-
Is Toxoplasma gondii playing a positive role in multiple sclerosis risk? A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neuroimmunol. 2018 Sep 15;322:57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Neuroimmunol. 2018. PMID: 29954625
-
Relationship between toxoplasmosis and obsessive compulsive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Apr 10;13(4):e0007306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007306. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30969961 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Headache: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(4):643-650. doi: 10.2174/1871526520666200617135851. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 32552646
Cited by
-
Relationship between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Depression in Clients of a Center for Assisted Reproduction.Pathogens. 2021 Aug 19;10(8):1052. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10081052. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34451515 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Brain and a History of Depression in Suicide Decedents: A Cross-Sectional Study.Pathogens. 2021 Oct 13;10(10):1313. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101313. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34684262 Free PMC article.
-
Association between latent toxoplasmosis and bipolar disorder: a case-control seroprevalence study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 2;25(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10405-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39743583 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii infection and risk of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathog Glob Health. 2020 May;114(3):117-126. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2020.1738153. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Pathog Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32186992 Free PMC article.
-
Infections, inflammation, and risk of neuropsychiatric disorders: the neglected role of "co-infection".Heliyon. 2020 Dec 8;6(12):e05645. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05645. eCollection 2020 Dec. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33319101 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

