Noninvasive glucose detection in exhaled breath condensate
- PMID: 31194942
- PMCID: PMC6783357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2019.05.006
Noninvasive glucose detection in exhaled breath condensate
Abstract
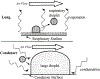
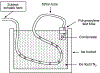
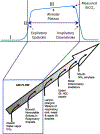
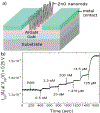
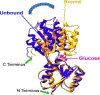
Two-thirds of patients with diabetes avoid regularly monitoring their blood glucose levels because of the painful and invasive nature of current blood glucose detection. As an alternative to blood sample collection, exhaled breath condensate (EBC) has emerged as a promising noninvasive sample from which to monitor glucose levels. However, this dilute sample matrix requires sensors capable of detecting glucose with high resolution at nanomolar and micromolar concentrations. Recent developments in EBC collection methods and highly sensitive glucose biosensors provide a path toward enabling robust and sensitive glucose detection in EBC. This review addresses current and emerging EBC collection and glucose sensing modalities capable of quantifying glucose in EBC samples. We highlight the opportunities and challenges for development and integration of EBC glucose detection systems that will enable clinically robust and accurate EBC glucose measurements for improved glycemic control.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
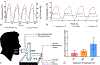
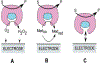
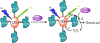


Similar articles
-
Selective Collection of Exhaled Breath Condensate for Noninvasive Screening of Breath Glucose.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2025 Jan;19(1):161-164. doi: 10.1177/19322968231179728. Epub 2023 Jul 4. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 37401788 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Collection and Condensation of Exhaled Breath for Glucose Detection.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:3890-3893. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8513393. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018. PMID: 30441212 Free PMC article.
-
A non-invasive method for the detection of glucose in human exhaled breath by condensation collection coupled with ion chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 2022 Dec 6;1685:463564. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463564. Epub 2022 Oct 17. J Chromatogr A. 2022. PMID: 36323098
-
Exhaled Breath Condensate: An Update.Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2018 Nov;38(4):667-678. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2018. PMID: 30342587 Review.
-
Exhaled breath condensate: an overview.Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2007 Nov;27(4):587-96; v. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2007.09.001. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2007. PMID: 17996577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Laser-Induced Carbon Nanofibers as Permeable Nonenzymatic Sensor for Biomarker Detection in Breath Aerosol.Anal Chem. 2025 Mar 4;97(8):4293-4298. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c06580. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39981995 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems in Digital Healthcare.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020 Sep;35(3):541-548. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.675. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32981296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancement in Biofluid-Based Glucose Sensors Using Invasive, Minimally Invasive, and Non-Invasive Technologies: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Mar 25;12(7):1082. doi: 10.3390/nano12071082. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of non-invasive detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory pathogens in exhaled breath condensate.J Breath Res. 2022 Mar 18;16(2):10.1088/1752-7163/ac59c7. doi: 10.1088/1752-7163/ac59c7. J Breath Res. 2022. PMID: 35235925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward Continuous Monitoring of Breath Biochemistry: A Paper-Based Wearable Sensor for Real-Time Hydrogen Peroxide Measurement in Simulated Breath.ACS Sens. 2019 Nov 22;4(11):2945-2951. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.9b01403. Epub 2019 Oct 25. ACS Sens. 2019. PMID: 31610653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Services USD of H and H, ed. National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and its Burden in the United States. 2014.
-
- Havas S Educational guidelines for achieving tight control and minimizing complications of type 1 diabetes. Am Fam Physician. 1999;60(7):1985–1992,1997–1998. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/10569502. - PubMed
-
- Kovalaske MA, Gandhi GY. Glycemic Control in the Medical Intensive Care Unit. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009;3(6):1330–1341. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2787033/. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

