Saikosaponin b2 enhances the hepatotargeting effect of anticancer drugs through inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated drug transporters
- PMID: 31194994
- PMCID: PMC7094655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116557
Saikosaponin b2 enhances the hepatotargeting effect of anticancer drugs through inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated drug transporters
Abstract
Aims: Vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri (VBRB) potentiates the activity of anticancer drugs in the liver by increasing their hepatic distribution. However, this phenomenon may be associated with drug transporters. We investigated the effect of saikosaponin b2 (SSb2; the main component of VBRB) on the activity and expression of different drug transporters in both normal cells and those that overexpress the transporter.
Main methods: The activities of transporters were analyzed by concentration of their cellular substrates. Concentrations of colchicine (substrate of Pgp and MRP1) and cisplatin (substrate of OCT2 and MRP2) were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The concentration of rhodamine B was determined by flow cytometry. The expression of transporter gene and protein were determined by qRT-PCR and Western blotting analysis.
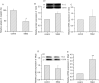
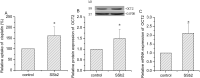
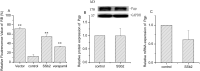
Key findings: SSb2 increased colchicine efflux in HEK293 cells by primarily increasing Mrp1 activity, independent of gene and protein expression. SSb2 enhanced Mrp2 function and increased cisplatin efflux in BRL3A cells by upregulating Mrp2 gene expression, with a marginal effect on Pgp in normal cells. SSb2 increased OCT2 activity in OCT2-HEK293 cells by increasing the expression of OCT2 protein and mRNA; however, SSb2 inhibited MRP2 activity in MRP2-HEK293 cells by decreasing MRP2 protein expression, and decreased Pgp and MRP1 activity in Pgp- and MRP1-HEK293 cells.
Significance: SSb2 might potentially be the key active component of VBRB that enhances the hepatotargeting of anticancer drugs through the inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated drug transporters (Pgp, MRP1, and MRP2) in an environment-dependent manner.
Keywords: Drug transporters; MRP; OCT2; Pgp; Saikosaponin b2.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Clerosterol from vinegar-baked radix bupleuri modifies drug transport.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):21351-21361. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15212. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423482 Free PMC article.
-
Saikosaponins A, C and D enhance liver-targeting effects of anticancer drugs by modulating drug transporters.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 23;8(66):110092-110102. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22639. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29299132 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of an ATP-binding cassette superfamily transporter, multidrug resistance protein 2, in human colorectal carcinomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Jun;6(6):2401-7. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10873092
-
Visualization of multidrug resistance in vivo.Eur J Nucl Med. 1999 Mar;26(3):283-93. doi: 10.1007/s002590050390. Eur J Nucl Med. 1999. PMID: 10079321 Review.
-
Multidrug resistance-associated protein: a protein distinct from P-glycoprotein involved in cytotoxic drug expulsion.Gen Pharmacol. 1997 May;28(5):639-45. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(96)00284-4. Gen Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9184795 Review.
Cited by
-
Zang Siwei Qingfei Mixture Alleviates Inflammatory Response to Attenuate Acute Lung Injury by the ACE2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(19):2871-2884. doi: 10.2174/0113862073259884231024111447. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37957855
-
Saikosaponin A and Its Epimers Alleviate LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice.Molecules. 2023 Jan 18;28(3):967. doi: 10.3390/molecules28030967. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770631 Free PMC article.
-
Natural product-derived phytochemicals as potential agents against coronaviruses: A review.Virus Res. 2020 Jul 15;284:197989. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.197989. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32360300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Effect of Aqueous and Methanolic Bupleuri Radix Extracts on Hepatic Uptake of High-Density Lipoprotein and Identification of the Potential Target in HFD-Fed Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Dec 5;2019:9074289. doi: 10.1155/2019/9074289. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31885672 Free PMC article.
-
Phytogenic Products and Phytochemicals as a Candidate Strategy to Improve Tolerance to Coronavirus.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Oct 20;7:573159. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.573159. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33195565 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheung F., Wang X., Wang N., Yuen M.F., Ziea T.C., Tong Y., Wong V.T., Feng Y. Chinese medicines as an adjuvant therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma during transarterial chemoembolization: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013;2013 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao R.Z., Chen Y.J., Cai J.X. Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops (BIBMW), 2011 IEEE International Conference on. 2011. Liver targeting effect of vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri on oxymatrine in mice; pp. 740–745.
-
- Zhao R.Z., Yuan D., Liu S.J., Chen Y.J., Liu L.J., Zhao Y. Liver targeting effect of vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri on rhein in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010;132:421–428. - PubMed
-
- Zhao R.Z., Liu S.J., Mao S.R., Wang Y.J. Study on liver targeting effect of vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri on resveratrol in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009;126:415–420. - PubMed
-
- Ye R.P., Chen Z.D. Saikosaponin A, an active glycoside from Radix bupleuri, reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in MCF-7/ADR cells and HepG2/ADM cells. Xenobiotica. 2017;47:176–184. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

