Effects of Transcranial Static Magnetic Stimulation on Motor Cortex Evaluated by Different TMS Waveforms and Current Directions
- PMID: 31195056
- PMCID: PMC6688472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.05.065
Effects of Transcranial Static Magnetic Stimulation on Motor Cortex Evaluated by Different TMS Waveforms and Current Directions
Abstract
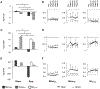
Transcranial static magnetic stimulation (tSMS) modulates cortical excitability probably by interacting with the GABA-glutamate intracortical balance. Different transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) waveforms probe distinct GABA-mediated cortical inhibition networks. The goal of the present work is to further characterize tSMS-induced changes in motor cortex reactivity and inhibition-excitation (I/E) balance. We hypothesized that tSMS affects particular cortical networks and thus, the effects of tSMS would be different depending on the TMS waveform used to assess its results. 23 healthy young adults completed two sessions of real or sham tSMS. The order of the sessions was randomized across participants. Motor evoked potentials (MEPs), cortical silent period (CSP), short- and long-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI and LICI), and intracortical facilitation (ICF) were assessed with TMS monophasic posterior-anterior (monoPA; n = 9), monophasic anterior-posterior (monoAP; n = 7), or biphasic (biAP-PA; n = 7) pulses. Repeated measures analyses of variance and appropriate pairwise comparisons were performed for each TMS measure. After 15 min of real tSMS, the MEP amplitudes decreased compared to sham and baseline, SICI and LICI showed greater inhibition, and a tendency towards longer CSPs and less facilitation was found. These results were only observed with monoPA TMS. MEP amplitude increased compared to sham with monoAP TMS, with no clear changes in general intracortical I/E balance. Biphasic TMS was not able to capture any effects of tSMS. The results show that the effects of tSMS on cortical excitability and inhibition involve specific interneuron circuits that are selectively activated by monoPA TMS.
Keywords: biphasic; current direction; monophasic; paired-pulse TMS; transcranial magnetic stimulation; transcranial static magnetic stimulation.
Copyright © 2019 IBRO. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
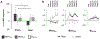
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Waveform and Current Direction on the Efficacy and Test-Retest Reliability of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation.Neuroscience. 2018 Nov 21;393:97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.09.044. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 30300705 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the cortical silent period elicited by single- and paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation.BMC Neurosci. 2013 Apr 2;14:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-14-43. BMC Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23547559 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of transcranial static magnetic stimulation on intracortical excitability in the contralateral primary motor cortex.Neurosci Lett. 2020 Apr 1;723:134871. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134871. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 32109553
-
Cortical excitability on sleep deprivation measured by transcranial magnetic stimulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Feb;221:111190. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2025.111190. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39756660
-
Motor potentials evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation: interpreting a simple measure of a complex system.J Physiol. 2023 Jul;601(14):2827-2851. doi: 10.1113/JP281885. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37254441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noninvasive modulation of human corticostriatal activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Apr 11;120(15):e2219693120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2219693120. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37023134 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Static Magnetic Field Stimulation on the Accuracy of Tachystoscopically Presented Line Bisection.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 18;10(12):1006. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10121006. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33352946 Free PMC article.
-
Different effects of I-wave periodicity repetitive TMS on motor cortex interhemispheric interaction.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 30;17:1079432. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1079432. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37457007 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity transcranial ultrasound stimulation facilitates hand motor function and cortical excitability: A crossover, randomized, double blind study.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 5;13:926027. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.926027. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36147048 Free PMC article.
-
Static magnetic stimulation induces structural plasticity at the axon initial segment of inhibitory cortical neurons.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 17;14(1):1479. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51845-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38233493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arias P, Adan-Arcay L, Puerta-Catoira B, Madrid A, Cudeiro J (2017) Transcranial static magnetic field stimulation of M1 reduces corticospinal excitability without distorting sensorimotor integration in humans. Brain Stimulat 10:340–342. - PubMed
-
- Biabani M, Farrell M, Zoghi M, Egan G, Jaberzadeh S (2018) The minimal number of TMS trials required for the reliable assessment of corticospinal excitability, short interval intracortical inhibition, and intracortical facilitation. Neurosci Lett 674:94–100. - PubMed
-
- Brasil-Neto JP, Cohen LG, Pascual-Leone A, Jabir FK, Wall RT, Hallett M (1992) Rapid reversible modulation of human motor outputs after transient deafferentation of the forearm: a study with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 42:1302–1306. - PubMed
-
- Cherubini E (2010) Phasic GABAA-mediated inhibition. Epilepsia 51:13–13. - PubMed
-
- Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Mazzone P, Insola A, Pilato F, Saturno E, Accurso A, Tonali P, Rothwell J (2001a) Comparison of descending volleys evoked by monophasic and biphasic magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex in conscious humans. Exp Brain Res 141:121–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

