High Resolution Imaging of Mouse Embryos and Neonates with X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography
- PMID: 31195428
- PMCID: PMC6594408
- DOI: 10.1002/cpmo.63
High Resolution Imaging of Mouse Embryos and Neonates with X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography
Abstract
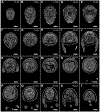
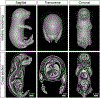
Iodine-contrast micro-computed tomography (microCT) 3D imaging provides a non-destructive and high-throughput platform for studying mouse embryo and neonate development. Here we provide protocols on preparing mouse embryos and neonates between embryonic day 8.5 (E8.5) to postnatal day 4 (P4) for iodine-contrast microCT imaging. With the implementation of the STABILITY method to create a polymer-tissue hybrid structure, we have demonstrated that not only is soft tissue shrinkage minimized but also the minimum required time for soft tissue staining with iodine is decreased, especially for E18.5 to P4 samples. In addition, we also provide a protocol on using commercially available X-CLARITYTM hydrogel solution to create the similar polymer-tissue hybrid structure on delicate early post-implantation stage (E8.5 to E14.5) embryos. With its simple sample staining and mounting processes, this protocol is easy to adopt and implement for most of the commercially available, stand-alone microCT systems in order to study mouse development between early post-implantation to early postnatal stages. © 2019 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Keywords: STABILITY; X-CLARITY; iodine contrasting; microCT.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Chung K, and Deisseroth K 2013. CLARITY for mapping the nervous system. Nature methods 10:508–513. - PubMed
-
- Ermakova O, Orsini T, Gambadoro A, Chiani F, and Tocchini-Valentini GP 2018. Three-dimensional microCT imaging of murine embryonic development from immediate post-implantation to organogenesis: application for phenotyping analysis of early embryonic lethality in mutant animals. Mammalian genome : official journal of the International Mammalian Genome Society 29:245–259. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

