E-cadherin Beyond Structure: A Signaling Hub in Colon Homeostasis and Disease
- PMID: 31195621
- PMCID: PMC6600153
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20112756
E-cadherin Beyond Structure: A Signaling Hub in Colon Homeostasis and Disease
Abstract
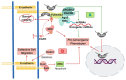
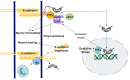
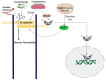
E-cadherin is the core component of epithelial adherens junctions, essential for tissue development, differentiation, and maintenance. It is also fundamental for tissue barrier formation, a critical function of epithelial tissues. The colon or large intestine is lined by an epithelial monolayer that encompasses an E-cadherin-dependent barrier, critical for the homeostasis of the organ. Compromised barriers of the colonic epithelium lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and are commonly observed in colorectal cancer. In addition to its architectural role, E-cadherin is also considered a tumor suppressor in the colon, primarily a result of its opposing function to Wnt signaling, the predominant driver of colon tumorigenesis. Beyond these well-established traditional roles, several studies have portrayed an evolving role of E-cadherin as a signaling epicenter that regulates cell behavior in response to intra- and extra-cellular cues. Intriguingly, these recent findings also reveal tumor-promoting functions of E-cadherin in colon tumorigenesis and new interacting partners, opening future avenues of investigation. In this Review, we focus on these emerging aspects of E-cadherin signaling, and we discuss their implications in colon biology and disease.
Keywords: CDH1; adherens junctions; cadherin; catenin; colon crypt; colorectal cancer; epithelial; inflammatory bowel disease; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of E-cadherin in epithelial barrier dysfunction: implications for bacterial infection, inflammation, and disease pathogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Feb 11;15:1506636. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1506636. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40007608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A key role for E-cadherin in intestinal homeostasis and Paneth cell maturation.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 14;5(12):e14325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014325. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21179475 Free PMC article.
-
E-cadherin is required for intestinal morphogenesis in the mouse.Dev Biol. 2012 Nov 1;371(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22766025 Free PMC article.
-
Autoregulation of E-cadherin expression by cadherin-cadherin interactions: the roles of beta-catenin signaling, Slug, and MAPK.J Cell Biol. 2003 Nov 24;163(4):847-57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200308162. Epub 2003 Nov 17. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14623871 Free PMC article.
-
Cadherin-catenin complex: protein interactions and their implications for cadherin function.J Cell Biochem. 1996 Jun 15;61(4):514-23. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19960616)61:4%3C514::AID-JCB4%3E3.0.CO;2-R. J Cell Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8806074 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated miRNA Inversely Correlates with E-cadherin Gene Expression in Tissue Biopsies from Crohn Disease Patients in contrast to Ulcerative Colitis Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 22;2020:4250329. doi: 10.1155/2020/4250329. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32775420 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis across aged tissues reveals distinct signatures and the crucial involvement of midgut barrier function in the regulation of aging.Aging Cell. 2025 Jan;24(1):e14344. doi: 10.1111/acel.14344. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 39319447 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-cell adhesions in embryonic stem cells regulate the stability and transcriptional activity of β-catenin.FEBS Lett. 2022 Jul;596(13):1647-1660. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14341. Epub 2022 Apr 6. FEBS Lett. 2022. PMID: 35344589 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers to Detect Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 25;10(2):255. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020255. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4+/IL‑4+ lymphocytes of the lamina propria and substance P promote colonic protection during acute stress.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Feb;25(2):63. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12579. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 34958108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noemi R., Dejana E. Adherens Junctions. Curr. Biol. 2008;18:R1080–R1082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

