Investigation of the Proportion of Diagnosed People Living with HIV/AIDS among Foreign Residents in Japan
- PMID: 31195745
- PMCID: PMC6616594
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8060804
Investigation of the Proportion of Diagnosed People Living with HIV/AIDS among Foreign Residents in Japan
Abstract
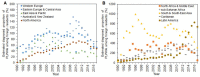
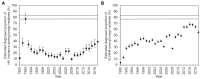
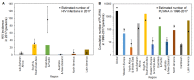
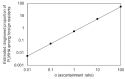
Foreign residents represent an increasing proportion of newly diagnosed human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) cases in Japan, though scant research has addressed this. This study aimed to estimate the diagnosed proportion of people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) among foreign residents in Japan, covering 1990-2017 and stratifying by geographic region of the country of origin. A balance equation model was employed to statistically estimate the diagnosed proportion as a single parameter. This used published estimates of HIV incidence and prevalence, population size, visit duration, travel volume, as well as surveillance data on HIV/AIDS in Japan. The proportion varied widely by region: People from Western Europe, East Asia and the Pacific, Australia and New Zealand, and North America were underdiagnosed, while those from sub-Saharan Africa, South and South-East Asia, and Latin America were more frequently diagnosed. Overall, the diagnosed proportion of PLWHA among foreign residents in Japan has increased, but the latest estimate in 2017 was as low as 55.3%; lower than the estimate among Japanese on the order of 80% and far below the quoted goal of 90%. This finding indicates a critical need to investigate the underlying mechanisms, including disparate access to HIV testing.
Keywords: antiretroviral therapy; epidemiology; foreigner; importation; laboratory diagnosis; migration; mobile men with money; test-and-treat; travel; treatment as prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global estimates of HIV infections and AIDS cases: 1991.AIDS. 1991;5 Suppl 2:S57-61. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199101001-00009. AIDS. 1991. PMID: 1845061
-
Epidemiology of HIV and AIDS in the Asia-Pacific region.Med J Aust. 1996 Nov 4;165(9):494-8. Med J Aust. 1996. PMID: 8937371 Review.
-
AIDS and sex tourism.AIDS Soc. 1992 Oct-Nov;4(1):1, 8. AIDS Soc. 1992. PMID: 12286016
-
One world, one hope: the cost of providing antiretroviral therapy to all nations.AIDS. 1998 Nov 12;12(16):2203-9. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199816000-00016. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9833862
-
[Socioeconomic aspects of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in developing countries].Bull Acad Natl Med. 1990 Nov;174(8):1209-19; discussion 1219-21. Bull Acad Natl Med. 1990. PMID: 2094555 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Estimation of the Actual Incidence of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Emergent Hotspots: The Example of Hokkaido, Japan during February-March 2020.J Clin Med. 2021 May 28;10(11):2392. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112392. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34071502 Free PMC article.
-
Measles and Rubella during COVID-19 Pandemic: Future Challenges in Japan.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 22;18(1):9. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010009. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33374998 Free PMC article.
-
A SWOT Analysis of the Guidelines on Prevention of HIV/AIDS in Japan in the Context of COVID-19.Infect Dis Rep. 2021 Nov 5;13(4):949-956. doi: 10.3390/idr13040087. Infect Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 34842732 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of coinfection with tuberculosis and HIV in Japan, 2012-2020.Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2022 Mar 28;13(1):1-8. doi: 10.5365/wpsar.2022.13.1.896. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2022. PMID: 35494412 Free PMC article.
-
The Extent of Transmission of Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China, 2020.J Clin Med. 2020 Jan 24;9(2):330. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020330. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 31991628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bavinton B.R., Pinto A.N., Phanuphak N., Grinsztejn B., Prestage G.P., Zablotska-Manos I.B., Jin F., Fairley C.K., Moore R., Roth N., et al. Viral suppression and HIV transmission in serodiscordant male couples: An international, prospective, observational, cohort study. Lancet HIV. 2018;5:e438–e447. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(18)30132-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS . Global HIV & AIDS Statistics—2018 Fact Sheet. UNAIDS; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018. [(accessed on 25 April 2019)]. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet.
Grants and funding
- H28-AIDS-General-001/Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- JP18fk0108050/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- 16KT0130, 16K15356, 17H04701, 17H05808 and 18H04895/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JPMJCR1413/Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology
- N/A/Inamori Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

