Drosophila Regnase-1 RNase is required for mRNA and miRNA profile remodelling during larva-to-adult metamorphosis
- PMID: 31195914
- PMCID: PMC6779395
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1630799
Drosophila Regnase-1 RNase is required for mRNA and miRNA profile remodelling during larva-to-adult metamorphosis
Abstract
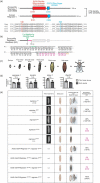
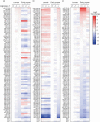
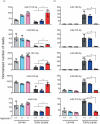
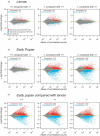
Metamorphosis is an intricate developmental process in which large-scale remodelling of mRNA and microRNA (miRNA) profiles leads to orchestrated tissue remodelling and organogenesis. Whether, which, and how, ribonucleases (RNases) are involved in the RNA profile remodelling during metamorphosis remain unknown. Human Regnase-1 (also known as MCPIP1 and Zc3h12a) RNase remodels RNA profile by cleaving specific RNAs and is a crucial modulator of immune-inflammatory and cellular defence. Here, we studied Drosophila CG10889, which we named Drosophila Regnase-1, an ortholog of human Regnase-1. The larva-to-adult metamorphosis in Drosophila includes two major transitions, larva-to-pupa and pupa-to-adult. regnase-1 knockout flies developed until the pupa stage but could not complete pupa-to-adult transition, dying in puparium case. Regnase-1 RNase activity is required for completion of pupa-to-adult transition as transgenic expression of wild-type Drosophila Regnase-1, but not the RNase catalytic-dead mutants, rescued the pupa-to-adult transition in regnase-1 knockout. High-throughput RNA sequencing revealed that regnase-1 knockout flies fail to remodel mRNA and miRNA profiles during the larva-to-pupa transition. Thus, we uncovered the roles of Drosophila Regnase-1 in the larva-to-adult metamorphosis and large-scale remodelling of mRNA and miRNA profiles during this metamorphosis process.
Keywords: RNase; Regnase-1; drosophila; mRNA; metamorphosis; miRNA.
Figures

References
-
- Thummel CS. Molecular mechanisms of developmental timing in C. elegans and Drosophila. Dev Cell. 2001;1(4): 453–465. PubMed PMID: 11703937. - PubMed
-
- White KP, Rifkin SA, Hurban P, et al. Microarray analysis of Drosophila development during metamorphosis. Science. 1999;286(5447): 2179–2184. PubMed PMID: 10591654. - PubMed
-
- Arbeitman MN, Furlong EE, Imam F, et al. Gene expression during the life cycle of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2002;297(5590):2270–2275. PubMed PMID: 12351791. - PubMed
-
- Cheadle C, Fan J, Cho-Chung YS, et al. Stability regulation of mRNA and the control of gene expression. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1058:196–204. PubMed PMID: 16394137. - PubMed
-
- Ling L, Ge X, Li Z, et al. MicroRNA let-7 regulates molting and metamorphosis in the silkworm, bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;53:13–21. PubMed PMID: 25016132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
