miR-122 promotes hepatic lipogenesis via inhibiting the LKB1/AMPK pathway by targeting Sirt1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 31195981
- PMCID: PMC6567918
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-019-0085-2
miR-122 promotes hepatic lipogenesis via inhibiting the LKB1/AMPK pathway by targeting Sirt1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common hepatic disease with an increasing prevalence but an unclear aetiology. This study aimed to investigate the functional implications of microRNA-122 (miR-122) in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and the possible molecular mechanisms.
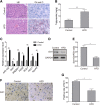
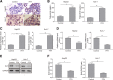
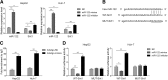
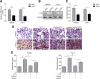
Methods: Both in vitro and in vivo models of NAFLD were generated by treating HepG2 and Huh-7 cells with free fatty acids (FFA) and by feeding mice a high-fat diet (HFD), respectively. HE and Oil Red O staining were used to examine liver tissue morphology and lipid deposition, respectively. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was used to examine Sirt1 expression in liver tissues. qRT-PCR and Western blotting were employed to measure the expression of miR-122, Sirt1, and proteins involved in lipogenesis and the AMPK pathway. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to quantify triglyceride (TG) levels in HepG2 and Huh-7 cells and in liver tissues. The interaction between miR-122 and the Sirt1 gene was further examined by a dual luciferase reporter assay and RNA-immunoprecipitation (RIP).
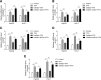
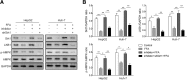
Results: NAFLD hepatic tissues and FFA-treated HepG2 and Huh-7 cells presented excess lipid production and TG secretion, accompanied by miR-122 upregulation, Sirt1 downregulation, and potentiated lipogenesis-related genes. miR-122 suppressed Sirt1 expression via binding to its 3'-untranslated region (UTR). Knockdown of miR-122 effectively mitigated excessive lipid production and suppressed the expression of lipogenic genes in FFA-treated HepG2 and Huh-7 cells via upregulating Sirt1. Furthermore, miR-122 knockdown activated the LKB1/AMPK signalling pathway.
Conclusion: The inhibition of miR-122 protects hepatocytes from lipid metabolic disorders such as NAFLD and suppresses lipogenesis via elevating Sirt1 and activating the AMPK pathway. These data support miR-122 as a promising biomarker and drug target for NAFLD.
Keywords: AMPK pathway; Lipogenesis; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Sirt1; miR-122.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circ_0057558 promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating ROCK1/AMPK signaling through targeting miR-206.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Aug 26;12(9):809. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04090-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34446693 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-H19 promotes hepatic lipogenesis by directly regulating miR-130a/PPARγ axis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jul 15;39(7):BSR20181722. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181722. Print 2019 Jul 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31064820 Free PMC article.
-
miR-34a regulates lipid metabolism by targeting SIRT1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with iron overload.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Nov 30;695:108642. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108642. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 33098868
-
Role of the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway in non‑alcoholic fatty liver disease (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2023 Feb;27(2):35. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12922. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36562343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural compounds against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A review on the involvement of the LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway.Phytother Res. 2023 Dec;37(12):5769-5786. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8020. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 37748097 Review.
Cited by
-
Signal Transduction and Molecular Regulation in Fatty Liver Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Sep 20;35(9):689-717. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0076. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 33906425 Free PMC article.
-
Schisandrin A Attenuates Diabetic Nephropathy via EGFR/AKT/GSK3β Signaling Pathway Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Biology (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;13(8):597. doi: 10.3390/biology13080597. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194535 Free PMC article.
-
The SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway mediates the anti-pulmonary fibrosis effect of liquiritigenin.Chin Med. 2024 Jan 18;19(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00886-1. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38238857 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for Health Functional Foods in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disorder (MASLD) Prevention: An Integrative Analysis of Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Multi-Omics.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 11;16(18):3061. doi: 10.3390/nu16183061. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Omics Nutritional Approaches Targeting Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;13(11):2142. doi: 10.3390/genes13112142. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akuta N, Kawamura Y, Suzuki F, Saitoh S, Arase Y, Fujiyama S, Sezaki H, Hosaka T, Kobayashi M, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, Ikeda K, Kumada H. Analysis of association between circulating miR-122 and histopathological features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients free of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016;16:141. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0557-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh E, Akbarzadeh A, Eslaminejad MB, Barzegar A, Hashemzadeh S, Nejati-Koshki K, Zarghami N. Up regulation of liver-enriched transcription factors HNF4a and HNF6 and liver-specific microRNA (miR-122) by inhibition of let-7b in mesenchymal stem cells. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2015;85:268–279. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12398. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brandt S, Roos J, Inzaghi E, Kotnik P, Kovac J, Battelino T, Cianfarani S, Nobili V, Colajacomo M, Kratzer W, Denzer C, Fischer-Posovszky P, Wabitsch M. Circulating levels of miR-122 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in pre-pubertal obese children. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13:175–182. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12261. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braza-Boils A, Mari-Alexandre J, Molina P, Arnau MA, Barcelo-Molina M, Domingo D, Girbes J, Giner J, Martinez-Dolz L, Zorio E. Deregulated hepatic microRNAs underlie the association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease. Liver Int. 2016;36:1221–1229. doi: 10.1111/liv.13097. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

