Efficacy of locally-delivered statins adjunct to non-surgical periodontal therapy for chronic periodontitis: a Bayesian network analysis
- PMID: 31196047
- PMCID: PMC6567452
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-019-0789-2
Efficacy of locally-delivered statins adjunct to non-surgical periodontal therapy for chronic periodontitis: a Bayesian network analysis
Abstract
Background: Studies indicate locally-delivered statins offer additional benefits to scaling and root planning (SRP), however, it is still hard to say which type of statins is better. This network meta-analysis aimed to assess the effect of locally-delivered statins and rank the most efficacious statin for treating chronic periodontitis (CP) in combination with SRP.
Methods: We screened four literature databases (Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science) for randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) published up to June 2018 that compared different statins in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. The outcomes analyzed were changes in intrabony defect depth (IBD), pocket depth (PD), and clinical attachment level (CAL). We carried out Bayesian network meta-analysis of CP without systemic diseases. Traditional and Bayesian network meta-analyses were conducted using random-effects models.
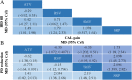
Results: Greater filling of IBD, reduction in PD, and gain in CAL were observed for SRP treated in combination with statins when compared to SRP alone for treating CP without systemic diseases. Specifically, SRP+ Atorvastatin (ATV) (mean difference [MD]: 1.5 mm, 1.4 mm, 1.8 mm, respectively), SRP + Rosuvastatin (RSV) (MD: 1.8 mm, 2.0 mm, 2.1 mm, respectively), and SRP + Simvastatin (SMV) (MD: 1.1 mm, 2.2 mm, 2.1 mm, respectively) were identified. However, no difference was found among the statins tested. In CP patients with type 2 diabetic (T2DM) or in smokers, additional benefits were observed from locally delivered statins.
Conclusion: Local statin use adjunctive to SRP confers additional benefits in treating CP by SRP, even in T2DM and smokers. RSV may be the best one to fill in IBD. However, considering the limitations of this study, clinicians must use cautious when applying the results and further studies are required to explore the efficacy of statins in CP with or without the risk factors (T2DM comorbidity or smoking history).
Keywords: Chronic periodontitis; Network meta-analysis; Periodontal therapy; Statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Locally applied statins as adjuvants to non-surgical periodontal treatment for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2018 Sep;22(7):2413-2430. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2507-x. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Clin Oral Investig. 2018. PMID: 29948277
-
Efficacy of statin delivery as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: A meta-analysis.J Investig Clin Dent. 2018 May;9(2):e12304. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12304. Epub 2017 Nov 9. J Investig Clin Dent. 2018. PMID: 29119729 Review.
-
Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on glycemic control of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2019 Aug 6;19(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12903-019-0829-y. BMC Oral Health. 2019. PMID: 31387569 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of subgingivally delivered simvastatin in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic periodontitis: a randomized double-masked controlled clinical trial.J Periodontol. 2013 Jan;84(1):24-31. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.110721. Epub 2012 Mar 16. J Periodontol. 2013. PMID: 22420871 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of locally delivered 1.2% rosuvastatin gel to non-surgical treatment of patients with chronic periodontitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial.J Periodontol. 2015 Jun;86(6):738-45. doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.140631. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Periodontol. 2015. PMID: 25786565 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Clinical Efficacy of 1.2% Rosuvastatin Hydrogel as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in Generalized Chronic Periodontitis.Cureus. 2024 May 24;16(5):e61008. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61008. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38910778 Free PMC article.
-
Local drug delivery in the treatment of furcation defects in periodontitis: a systematic review.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Mar;27(3):955-970. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-04871-0. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 36729235 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin Accelerates Alveolar Bone Loss in Type 1 Diabetic Rats Submitted to Periodontitis.Braz Dent J. 2024 Oct 28;35:e246100. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440202406100. eCollection 2024. Braz Dent J. 2024. PMID: 39476053 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-gingival delivery of simvastatin and rosuvastatin for treatment of chronic periodontitis with diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled clinical-radiographic pilot study.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023 Mar-Apr;13(2):315-320. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2023.02.012. Epub 2023 Mar 3. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023. PMID: 36891284 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Applying Atorvastatin 1.2% Bio Adhesive with Plasma Rich in Growth Factor (PRGF) for Treatment of Mandibular Class II Furcation Defects: a Randomized Clinical Trial.J Dent (Shiraz). 2022 Jun;23(2):86-94. doi: 10.30476/DENTJODS.2021.84581.1090. J Dent (Shiraz). 2022. PMID: 35783501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vergnes JN, Canceill T, Vinel A, Laurencin-Dalicieux S, Maupas-Schwalm F, Blasco-Baque V, Hanaire H, Arrive E, Rigalleau V, Nabet C, et al. The effects of periodontal treatment on diabetic patients: the DIAPERIO randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(10):1150–1163. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

