A preclinical study-systemic evaluation of safety on mesenchymal stem cells derived from human gingiva tissue
- PMID: 31196163
- PMCID: PMC6567625
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1262-5
A preclinical study-systemic evaluation of safety on mesenchymal stem cells derived from human gingiva tissue
Abstract
Background: Mounting evidence has shown that a novel subset of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from human gingiva referred to as gingival mesenchymal stem cells (GMSCs) displays a greater immunotherapeutic potential and regenerative repair expression than MSCs obtained from other tissues. However, the safety of the use of transplanted GMSCs in humans remains unclear.
Methods: In this study, we evaluated the safety of GMSCs transplanted into mouse, rat, rabbit, beagle dog, and monkey as well as two animal models of autoimmune diseases.
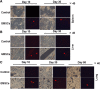
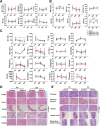
Results: In short- and long-term toxicity tests, infused GMSCs had no remarkable adverse effects on hematologic and biochemical indexes, particularly on the major organs such as heart, liver, spleen, and kidney in recipient animals. It was also shown that GMSCs were well tolerated in other assays including hemolysis, vascular, and muscular stimulation, as well as systemic anaphylaxis and passive skin Arthus reaction in animal models. GSMC infusion did not cause any notable side effects on animal models of either autoimmune arthritis or lupus. Significantly, GMSCs most likely play no role in genotoxicity and tumorigenesis. The biological features remained stable for an extended period after cell transfer.
Conclusions: GMSCs are safe in various animal models of autoimmunity, even during active disease episodes, especially in monkeys. This study paves a solid road for future clinical trials of GMSCs in patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Gingival mesenchymal stem cells (GMSCs); Mesenchymal stromal cell; Safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Updates on GMSCs Treatment for Autoimmune Diseases.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(5):345-349. doi: 10.2174/1574888X13666180220141114. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29468980 Review.
-
Gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cell-mediated therapeutic approach for bone tissue regeneration.Stem Cells Dev. 2011 Dec;20(12):2093-102. doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0523. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Stem Cells Dev. 2011. PMID: 21361847
-
Treatment of gingival defects with gingival mesenchymal stem cells derived from human fetal gingival tissue in a rat model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Feb 5;9(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0751-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29402326 Free PMC article.
-
Stemness Potency of Human Gingival Cells-Application in Anticancer Therapies and Clinical Trials.Cells. 2020 Aug 18;9(8):1916. doi: 10.3390/cells9081916. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32824702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Periodontal Regenerative Substitute.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Jan;22(1):1-21. doi: 10.1007/s13770-024-00676-8. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 39607668 Review.
Cited by
-
A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from human gingival tissue.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2019 Aug 15;8(4):21-26. eCollection 2019. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31497379 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Cytokine Storm due to COVID-19.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Nov 26;2021:3178796. doi: 10.1155/2021/3178796. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34840969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psoriasis treatment using minimally manipulated umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Aug 16;9(23):6798-6803. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6798. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 34447827 Free PMC article.
-
Gingival-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate allergic asthma inflammation via HGF in animal models.iScience. 2024 Apr 26;27(5):109818. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109818. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38766356 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-148a-containing GMSC-derived EVs modulate Treg/Th17 balance via IKKB/NF-κB pathway and treat a rheumatoid arthritis model.JCI Insight. 2024 Apr 23;9(10):e177841. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.177841. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38652539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen M, Su W, Lin X, et al. Adoptive transfer of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis via suppression of Th1 and Th17 cells and enhancement of regulatory T cell differentiation. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:1181–1193. doi: 10.1002/art.37894. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

