Contribution of Gene Regulatory Networks to Heritability of Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 31196451
- PMCID: PMC6590059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.520
Contribution of Gene Regulatory Networks to Heritability of Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
Background: Genetic variants currently known to affect coronary artery disease (CAD) risk explain less than one-quarter of disease heritability. The heritability contribution of gene regulatory networks (GRNs) in CAD, which are modulated by both genetic and environmental factors, is unknown.
Objectives: This study sought to determine the heritability contributions of single nucleotide polymorphisms affecting gene expression (eSNPs) in GRNs causally linked to CAD.
Methods: Seven vascular and metabolic tissues collected in 2 independent genetics-of-gene-expression studies of patients with CAD were used to identify eSNPs and to infer coexpression networks. To construct GRNs with causal relations to CAD, the prior information of eSNPs in the coexpression networks was used in a Bayesian algorithm. Narrow-sense CAD heritability conferred by the GRNs was calculated from individual-level genotype data from 9 European genome-wide association studies (GWAS) (13,612 cases, 13,758 control cases).
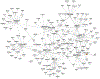
Results: The authors identified and replicated 28 independent GRNs active in CAD. The genetic variation in these networks contributed to 10.0% of CAD heritability beyond the 22% attributable to risk loci identified by GWAS. GRNs in the atherosclerotic arterial wall (n = 7) and subcutaneous or visceral abdominal fat (n = 9) were most strongly implicated, jointly explaining 8.2% of CAD heritability. In all, these 28 GRNs (each contributing to >0.2% of CAD heritability) comprised 24 to 841 genes, whereof 1 to 28 genes had strong regulatory effects (key disease drivers) and harbored many relevant functions previously associated with CAD. The gene activity in these 28 GRNs also displayed strong associations with genetic and phenotypic cardiometabolic disease variations both in humans and mice, indicative of their pivotal roles as mediators of gene-environmental interactions in CAD.
Conclusions: GRNs capture a major portion of genetic variance and contribute to heritability beyond that of genetic loci currently known to affect CAD risk. These networks provide a framework to identify novel risk genes/pathways and study molecular interactions within and across disease-relevant tissues leading to CAD.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; gene regulatory networks; heritability; systems genetics.
Copyright © 2019 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
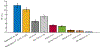
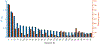


Comment in
-
Gene Regulatory Networks to Explain Coronary Artery Disease Heritability.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jun 18;73(23):2958-2960. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.511. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31196452 No abstract available.
References
-
- Marenberg ME, Risch N, Berkman LF, Floderus B, de Faire U. Genetic susceptibility to death from coronary heart disease in a study of twins. N Engl J Med. 1994. April 14;330(15):1041–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K23 HL111339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL135289/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130423/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 TR001739/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- BB/J004235/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/M020053/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL071207/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG050986/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL111330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

