A Rare Deep-Rooting D0 African Y-Chromosomal Haplogroup and Its Implications for the Expansion of Modern Humans Out of Africa
- PMID: 31196864
- PMCID: PMC6707464
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.119.302368
A Rare Deep-Rooting D0 African Y-Chromosomal Haplogroup and Its Implications for the Expansion of Modern Humans Out of Africa
Abstract
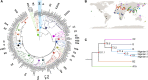
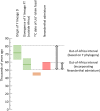
Present-day humans outside Africa descend mainly from a single expansion out ∼50,000-70,000 years ago, but many details of this expansion remain unclear, including the history of the male-specific Y chromosome at this time. Here, we reinvestigate a rare deep-rooting African Y-chromosomal lineage by sequencing the whole genomes of three Nigerian men described in 2003 as carrying haplogroup DE* Y chromosomes, and analyzing them in the context of a calibrated worldwide Y-chromosomal phylogeny. We confirm that these three chromosomes do represent a deep-rooting DE lineage, branching close to the DE bifurcation, but place them on the D branch as an outgroup to all other known D chromosomes, and designate the new lineage D0. We consider three models for the expansion of Y lineages out of Africa ∼50,000-100,000 years ago, incorporating migration back to Africa where necessary to explain present-day Y-lineage distributions. Considering both the Y-chromosomal phylogenetic structure incorporating the D0 lineage, and published evidence for modern humans outside Africa, the most favored model involves an origin of the DE lineage within Africa with D0 and E remaining there, and migration out of the three lineages (C, D, and FT) that now form the vast majority of non-African Y chromosomes. The exit took place 50,300-81,000 years ago (latest date for FT lineage expansion outside Africa - earliest date for the D/D0 lineage split inside Africa), and most likely 50,300-59,400 years ago (considering Neanderthal admixture). This work resolves a long-running debate about Y-chromosomal out-of-Africa/back-to-Africa migrations, and provides insights into the out-of-Africa expansion more generally.
Keywords: Human Y chromosome; YAP+ Y chromosomes; out-of-Africa migration; phylogeography.
Copyright © Haber et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Southeast Asian origin for present-day non-African human Y chromosomes.Hum Genet. 2021 Feb;140(2):299-307. doi: 10.1007/s00439-020-02204-9. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 32666166 Free PMC article.
-
Carriers of mitochondrial DNA macrohaplogroup L3 basal lineages migrated back to Africa from Asia around 70,000 years ago.BMC Evol Biol. 2018 Jun 19;18(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12862-018-1211-4. BMC Evol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29921229 Free PMC article.
-
Rare deep-rooting Y chromosome lineages in humans: lessons for phylogeography.Genetics. 2003 Sep;165(1):229-34. doi: 10.1093/genetics/165.1.229. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 14504230 Free PMC article.
-
Trend of different molecular markers in the last decades for studying human migrations.Gene. 2015 Feb 10;556(2):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.12.023. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25510397 Review.
-
Phylogeographic review of Y chromosome haplogroups in Europe.Int J Legal Med. 2021 Sep;135(5):1675-1684. doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02644-6. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Int J Legal Med. 2021. PMID: 34216266 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial and temporal diversity of positive selection on shared haplotypes at the PSCA locus among worldwide human populations.Heredity (Edinb). 2023 Aug;131(2):156-169. doi: 10.1038/s41437-023-00631-8. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Heredity (Edinb). 2023. PMID: 37353592 Free PMC article.
-
An update and frequency distribution of Y chromosome haplogroups in modern Japanese males.J Hum Genet. 2024 Apr;69(3-4):107-114. doi: 10.1038/s10038-023-01214-5. Epub 2023 Dec 21. J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38123667
-
A Genetic History of the Near East from an aDNA Time Course Sampling Eight Points in the Past 4,000 Years.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Jul 2;107(1):149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.05.008. Epub 2020 May 28. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32470374 Free PMC article.
-
Origins of modern human ancestry.Nature. 2021 Feb;590(7845):229-237. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03244-5. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33568824 Review.
-
A Genetic Variation in the Y Chromosome Among Modern Japanese Males Related to Several Physiological and Psychological Characteristics.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Dec 2;15:774879. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.774879. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34924970 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

