Nitration-induced ubiquitination and degradation control quality of ERK1
- PMID: 31196894
- PMCID: PMC6604951
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20190240
Nitration-induced ubiquitination and degradation control quality of ERK1
Abstract
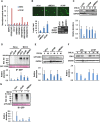
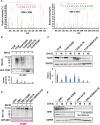
The mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK1/2 (ERKs, extracellular-regulated protein kinases) plays important roles in a wide spectrum of cellular processes and have been implicated in many disease states. The spatiotemporal regulation of ERK activity has been extensively studied. However, scarce information has been available regarding the quality control of the kinases to scavenge malfunctioning ERKs. Using site-specific mutagenesis and mass spectrometry, we found that the disruption of the conserved H-bond between Y210 and E237 of ERK1 through point mutation at or naturally occurring nitration on Y210 initiates a quality control program dependent on chaperon systems and CHIP (C-terminal of Hsp70-interacting protein)-mediated ubiquitination and degradation. The H-bond is also important for the quality control of ERK2, but through a distinct mechanism. These findings clearly demonstrate how malfunctioning ERKs are eliminated when cells are in certain stress conditions or unhealthy states, and could represent a general mechanism for scavenging malfunctioning kinases in stress conditions.
Keywords: ERK; mass spectrometry; phosphorylation; quality control; tyrosine nitration; ubiquitination.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The PHD domain of MEKK1 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and mediates ubiquitination and degradation of ERK1/2.Mol Cell. 2002 May;9(5):945-56. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00519-1. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12049732
-
Regulatory roles of conserved phosphorylation sites in the activation T-loop of the MAP kinase ERK1.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Mar 15;27(6):1040-50. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-07-0527. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26823016 Free PMC article.
-
A cellular threshold for active ERK1/2 levels determines Raf/MEK/ERK-mediated growth arrest versus death responses.Cell Signal. 2018 Jan;42:11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 28986121 Free PMC article.
-
The ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of the G1- to S-phase transition.Oncogene. 2007 May 14;26(22):3227-39. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210414. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17496918 Review.
-
ERK1/2 MAP kinases: structure, function, and regulation.Pharmacol Res. 2012 Aug;66(2):105-43. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.04.005. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 22569528 Review.
Cited by
-
Chaperone-assisted E3 ligase CHIP: A double agent in cancer.Genes Dis. 2021 Sep 1;9(6):1521-1555. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.08.003. eCollection 2022 Nov. Genes Dis. 2021. PMID: 36157498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Pain-Specific Gene Expression Profile for Pediatric Recurrent Abdominal Pain.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 5;2:759634. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2021.759634. eCollection 2021. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 35295473 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a TSR-Based Method for Protein 3-D Structural Comparison With Its Applications to Protein Classification and Motif Discovery.Front Chem. 2021 Jan 13;8:602291. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.602291. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33520934 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM15 and CYLD regulate ERK activation via lysine-63-linked polyubiquitination.Nat Cell Biol. 2021 Sep;23(9):978-991. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00732-8. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Nat Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34497368 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Tyrosine Nitration in Plant Nitric Oxide Signaling.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 11;13:859374. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.859374. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35360296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

