Up-regulation of FOXO1 and reduced inflammation by β-hydroxybutyric acid are essential diet restriction benefits against liver injury
- PMID: 31196960
- PMCID: PMC6613133
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1820282116
Up-regulation of FOXO1 and reduced inflammation by β-hydroxybutyric acid are essential diet restriction benefits against liver injury
Abstract
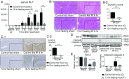
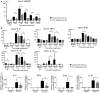
Liver ischemia and reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major challenge in liver surgery. Diet restriction reduces liver damage by increasing stress resistance; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated the preventive effect of 12-h fasting on mouse liver IRI. Partial warm hepatic IRI model in wild-type male C57BL/6 mice was used. The control ischemia and reperfusion (IR) group of mice was given food and water ad libitum, while the fasting IR group was given water but not food for 12 h before ischemic insult. In 12-h fasting mice, serum liver-derived enzyme level and tissue damages due to IR were strongly suppressed. Serum β-hydroxybutyric acid (BHB) was significantly raised before ischemia and during reperfusion. Up-regulated BHB induced an increment in the expression of FOXO1 transcription factor by raising the level of acetylated histone. Antioxidative enzyme heme oxigenase 1 (HO-1), a target gene of FOXO1, then increased. Autophagy activity was also enhanced. Serum high-mobility group box 1 was remarkably lowered by the 12-h fasting, and activation of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome was suppressed. Consequently, inflammatory cytokine production and liver injury were reduced. Exogenous BHB administration or histone deacetylase inhibitor administration into the control fed mice ameliorated liver IRI, while FOXO1 inhibitor administration to the 12-h fasting group exacerbated liver IRI. The 12-h fasting exerted beneficial effects on the prevention of liver IRI by increasing BHB, thus up-regulating FOXO1 and HO-1, and by reducing the inflammatory responses and apoptotic cell death via the down-regulation of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome.
Keywords: FOXO1; fasting; ischemia and reperfusion injury; β-hydroxybutyric acid.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 regulates toll-like receptor 4 innate responses in mouse liver ischemia-reperfusion injury through Akt-forkhead box protein O1 signaling network.Transplantation. 2014 Oct 15;98(7):721-8. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000316. Transplantation. 2014. PMID: 25171655 Free PMC article.
-
Remimazolam alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating FOXO1/3 signaling : Remimazolam alleviates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 22;25(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03820-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40263992 Free PMC article.
-
Liver kinase B1 attenuates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Apr 15;53(5):601-611. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab030. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33783473
-
Initiation of the inflammatory response after renal ischemia/reperfusion injury during renal transplantation.Int Urol Nephrol. 2018 Nov;50(11):2027-2035. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-1918-6. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29974405 Review.
-
Does Calorie Restriction Modulate Inflammaging via FoxO Transcription Factors?Nutrients. 2020 Jun 30;12(7):1959. doi: 10.3390/nu12071959. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32630045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise Ameliorates Atherosclerosis via Up-Regulating Serum β-Hydroxybutyrate Levels.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 30;23(7):3788. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073788. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409148 Free PMC article.
-
β-Hydroxybutyrate as an epigenetic modifier: Underlying mechanisms and implications.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 17;9(11):e21098. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21098. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37928021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-hydroxybutyrate administration improves liver injury and metabolic abnormality in postnatal growth retardation piglets.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 3;10:1294095. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1294095. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38026634 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of DYRK1B suppresses inflammation in allergic contact dermatitis model and Th1/Th17 immune response.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 29;13(1):7058. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34211-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37120440 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnane X receptor knockout mitigates weight gain and hepatic metabolic dysregulation in female C57BL/6 J mice on a long-term high-fat diet.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Apr;173:116341. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116341. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38428309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Serracino-Inglott F., Habib N. A., Mathie R. T., Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Surg. 181, 160–166 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Farmer D. G., Amersi F., Kupiec-Weglinski J., Busuttil R. W., Current status of ischemia and reperfusion injury in the liver. Transplant. Rev. 14, 106–126 (2000).
-
- Klune J. R., Tsung A., Molecular biology of liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: Established mechanisms and recent advancements. Surg. Clin. North Am. 90, 665–677 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

