Discovery and characterization of natural products as novel indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitors through high-throughput screening
- PMID: 31197246
- PMCID: PMC7468576
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-019-0246-4
Discovery and characterization of natural products as novel indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitors through high-throughput screening
Abstract
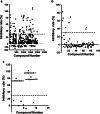
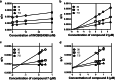
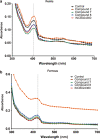
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is emerging as a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of malignant tumors characterized by dysregulated tryptophan metabolism. However, the antitumor efficacy of existing small-molecule IDO1 inhibitors is still unsatisfactory, and the underlying mechanism remains largely undefined. To identify novel IDO1 inhibitors, an in-house natural product library of 2000 natural products was screened for inhibitory activity against recombinant human IDO1. High-throughput fluorescence-based screening identified 79 compounds with inhibitory activity > 30% at 20 μM. Nine natural products were further confirmed to inhibit IDO1 activity by > 30% using Ehrlich's reagent reaction. Compounds 2, 7, and 8 were demonstrated to inhibit IDO1 activity in a cellular context. Compounds 2 and 7 were more potent against IDO1 than TDO2 in the enzymatic assay. The kinetic studies showed that compound 2 exhibited noncompetitive inhibition, whereas compounds 7 and 8 were graphically well matched with uncompetitive inhibition. Compounds 7 and 8 were found to bind to the ferric-IDO1 enzyme. Docking stimulations showed that the naphthalene ring of compound 8 formed "T-shaped" π-π interactions with Phe-163 and that the 6-methyl-naphthalene group formed additional hydrophobic interactions with IDO1. Compound 8 was identified as a derivative of tanshinone, and preliminary SAR analysis indicated that tanshinone derivatives may be promising hits for the development of IDO1 inhibitors. This study provides new clues for the discovery of IDO1/TDO2 inhibitors with novel scaffolds.
Keywords: high-throughput fluorescence-based screening; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitor; natural product library.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Discovery and Characterisation of Dual Inhibitors of Tryptophan 2,3-Dioxygenase (TDO2) and Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) Using Virtual Screening.Molecules. 2019 Nov 28;24(23):4346. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234346. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31795096 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and comparison of the commonly used bioassays of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO).Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104348. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104348. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33142415
-
Synthesis of novel tryptanthrin derivatives as dual inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020 Jun 1;30(11):127159. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127159. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32247733
-
Challenges in the Discovery of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2015 Dec 24;58(24):9421-37. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00326. Epub 2015 May 26. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25970480 Review.
-
Recent discovery of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitors targeting cancer immunotherapy.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:656-669. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.088. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29220788 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteins and DNA Sequences Interacting with Tanshinones and Tanshinone Derivatives.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 20;26(2):848. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020848. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitory compounds from natural sources.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 4;13:1046818. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1046818. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36408235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Immune Modulators Enhance Caenorhabditis elegans Resistance to Multiple Pathogens.mSphere. 2021 Jan 6;6(1):e00950-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00950-20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33408224 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate as a Potent IDO1/TDO2 Dual Inhibitor Enhances Anti-PD1 Therapy for Colorectal Cancer in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 27;13:870848. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.870848. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35571116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moffett JR, Namboodiri MA. Tryptophan and the immune response. Immunol Cell Biol. 2003;81:247–65. - PubMed
-
- Munn DH, Zhou M, Attwood JT, Bondarev I, Conway SJ, Marshall B, et al. Prevention of allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science. 1998;281:1191–3. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto A, Nikaido T, Ochiai K, Takakura S, Saito M, Aoki Y, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase serves as a marker of poor prognosis in gene expression profiles of serous ovarian cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6030–9. - PubMed
-
- Uyttenhove C, Pilotte L, Theate I, Stroobant V, Colau D, Parmentier N, et al. Evidence for a tumoral immune resistance mechanism based on tryptophan degradation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Nat Med. 2003;9:1269–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

