Cloud bursting galaxy: federated identity and access management
- PMID: 31197310
- PMCID: PMC6956780
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz472
Cloud bursting galaxy: federated identity and access management
Abstract
Motivation: Large biomedical datasets, such as those from genomics and imaging, are increasingly being stored on commercial and institutional cloud computing platforms. This is because cloud-scale computing resources, from robust backup to high-speed data transfer to scalable compute and storage, are needed to make these large datasets usable. However, one challenge for large-scale biomedical data on the cloud is providing secure access, especially when datasets are distributed across platforms. While there are open Web protocols for secure authentication and authorization, these protocols are not in wide use in bioinformatics and are difficult to use for even technologically sophisticated users.
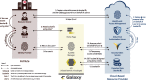
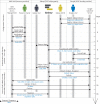
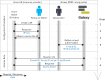
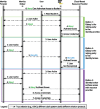
Results: We have developed a generic and extensible approach for securely accessing biomedical datasets distributed across cloud computing platforms. Our approach combines OpenID Connect and OAuth2, best-practice Web protocols for authentication and authorization, together with Galaxy (https://galaxyproject.org), a web-based computational workbench used by thousands of scientists across the world. With our enhanced version of Galaxy, users can access and analyze data distributed across multiple cloud computing providers without any special knowledge of access/authorization protocols. Our approach does not require users to share permanent credentials (e.g. username, password, API key), instead relying on automatically generated temporary tokens that refresh as needed. Our approach is generalizable to most identity providers and cloud computing platforms. To the best of our knowledge, Galaxy is the only computational workbench where users can access biomedical datasets across multiple cloud computing platforms using best-practice Web security approaches and thereby minimize risks of unauthorized data access and credential use.
Availability and implementation: Freely available for academic and commercial use under the open-source Academic Free License (https://opensource.org/licenses/AFL-3.0) from the following Github repositories: https://github.com/galaxyproject/galaxy and https://github.com/galaxyproject/cloudauthz.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Federated Galaxy: Biomedical Computing at the Frontier.IEEE Int Conf Cloud Comput. 2018 Jul;2018:10.1109/cloud.2018.00124. doi: 10.1109/cloud.2018.00124. Epub 2018 Sep 10. IEEE Int Conf Cloud Comput. 2018. PMID: 34386295 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics Virtual Laboratory: A Practical Bioinformatics Workbench for the Cloud.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 26;10(10):e0140829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140829. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26501966 Free PMC article.
-
Swarm: A federated cloud framework for large-scale variant analysis.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 May 12;17(5):e1008977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008977. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33979321 Free PMC article.
-
Cloud-based biomedical data storage and analysis for genomic research: Landscape analysis of data governance in emerging NIH-supported platforms.HGG Adv. 2023 Apr 12;4(3):100196. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2023.100196. eCollection 2023 Jul 13. HGG Adv. 2023. PMID: 37181330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving data workflow systems with cloud services and use of open data for bioinformatics research.Brief Bioinform. 2018 Sep 28;19(5):1035-1050. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx039. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 28419324 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GA4GH Passport standard for digital identity and access permissions.Cell Genom. 2021 Nov 10;1(2):None. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2021.100030. Cell Genom. 2021. PMID: 34820660 Free PMC article.
-
The GA4GH Task Execution Application Programming Interface: Enabling Easy Multicloud Task Execution.Comput Sci Eng. 2024 Jul-Sep;26(3):30-39. doi: 10.1109/mcse.2024.3414994. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Comput Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 40792191 Free PMC article.
-
The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2020 update.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jul 2;48(W1):W395-W402. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa434. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32479607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basney J. et al. (2014) Cilogon: a federated x. 509 certification authority for cyberinfrastructure logon. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp., 26, 2225–2239.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

