Long-term exposure to a 40-GHz electromagnetic field does not affect genotoxicity or heat shock protein expression in HCE-T or SRA01/04 cells
- PMID: 31197350
- PMCID: PMC6640906
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrz017
Long-term exposure to a 40-GHz electromagnetic field does not affect genotoxicity or heat shock protein expression in HCE-T or SRA01/04 cells
Abstract
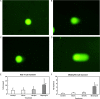
Millimeter waves are used in various fields, and the risks of this wavelength range for human health must be carefully evaluated. In this study, we investigated the effects of millimeter waves on genotoxicity and heat shock protein expression in human corneal epithelial (HCE-T) and human lens epithelial (SRA01/04) cells. We exposed the cells to 40-GHz millimeter waves at 1 mW/cm2 for 24 h. We observed no statistically significant increase in the micronucleus (MN) frequency or the level of DNA strand breaks in cells exposed to 40-GHz millimeter waves relative to sham-exposed and incubator controls. Heat shock protein (Hsp) expression also exhibited no statistically significant response to the 40-GHz exposure. These results indicate that exposure to 40 GHz millimeter waves under these conditions has little or no effect on MN formation, DNA strand breaks, or Hsp expression in HCE-T or SRA01/04 cells.
Keywords: comet assay; heat shock protein; human eye cells; micronucleus formation; millimeter waves.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japan Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Long-Term Exposure to 60 GHz Millimeter-Wavelength Radiation on the Genotoxicity and Heat Shock Protein (Hsp) Expression of Cells Derived from Human Eye.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Aug 8;13(8):802. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13080802. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27509516 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty Four-Hour Exposure to a 0.12 THz Electromagnetic Field Does Not Affect the Genotoxicity, Morphological Changes, or Expression of Heat Shock Protein in HCE-T Cells.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Aug 5;13(8):793. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13080793. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27527204 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Exposure to 5.8 GHz Electromagnetic Field on Micronucleus Formation, DNA Strand Breaks, and Heat Shock Protein Expressions in Cells Derived From Human Eye.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2019 Apr;18(2):257-260. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2019.2905491. Epub 2019 Mar 15. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2019. PMID: 30892224
-
Effects of 1.8 GHz radiofrequency field on DNA damage and expression of heat shock protein 70 in human lens epithelial cells.Mutat Res. 2006 Dec 1;602(1-2):135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.08.010. Epub 2006 Oct 2. Mutat Res. 2006. PMID: 17011595
-
[Effect of long-term power frequency electromagnetic field exposure on proliferation and apoptosis of SRA01/04 cells].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;31(4):246-50. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23595299 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Advances in Millimeter-Wave Treatment and Its Biological Effects Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8638. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168638. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5G mobile networks and health-a state-of-the-science review of the research into low-level RF fields above 6 GHz.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2021 Jul;31(4):585-605. doi: 10.1038/s41370-021-00297-6. Epub 2021 Mar 16. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2021. PMID: 33727687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang X, Chen M, Zhou J et al. . HSP27, 70 and 90, anti-apoptotic proteins, in clinical cancer therapy (Review). Int J Clin Oncol 2014;45:18–30. - PubMed
-
- Beneduci A, Chidichimo G, De Rose R et al. . Frequency and irradiation time-dependent antiprolifirative effect of low-power millimetre waves on RPMI 7932 human melanoma cell line. Anticancer Res 2005;25:1023–8. - PubMed
-
- Korenstein-Ilan A, Barbul A, Hasin P et al. . Terahertz radiation increases genomic instability in human lymphocytes. Radiat Res 2008;170:224–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

