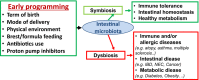
Paediatricians play a key role in preventing early harmful events that could permanently influence the development of the gut microbiota in childhood
- PMID: 31197890
- PMCID: PMC6852013
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.14900
Paediatricians play a key role in preventing early harmful events that could permanently influence the development of the gut microbiota in childhood
Abstract
Aim: The development of the gut microbiota occurs primarily during infancy, and growing evidence has emphasised its positive role and implications for human health. The aim of this review was to provide essential knowledge about the gut microbiota and to describe and highlight the importance of the factors that influence the gut microbiota in early life and their potential harmful effects later in life.
Methods: The European Paediatric Association, the Union of the National European Paediatric Societies and Associations, convened a panel of independent European experts to summarise the research on microbiota for general paediatricians. They used PubMed and the Cochrane Library to identify studies published in English up to June 2018.
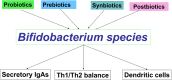
Results: A number of clinical conditions can disrupt the development of a stable gut microbiota. Changes in the microbiome have been documented in many chronic diseases, mainly immune-mediated gastrointestinal and liver diseases, and distinct patterns have been associated with each specific disease. The gut microbiota can be positively modulated with probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, paraprobiotics and postbiotics.
Conclusion: Paediatricians can play a key role in preventing harmful events that could permanently influence the composition and/or function of the gut microbiota. Various treatment strategies can be used.
Keywords: Dysbiosis; Gut microbiota; Prebiotics; Probiotics; Synbiotics.
©2019 The Authors. Acta Paediatrica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Foundation Acta Paediatrica.
Conflict of interest statement
Sanja Kolaček has received lecture fees, travel grants and unrestrained support for the hospital from Abbott, AbVie, BioGaia, Fresenius, Medis, Nestle, Nutricia. Iva Hojsak has received lecture fees and consultation fees from BioGaia, Medis, Nestle, Nutricia, Fresenius Kabi and Chr Hansen.
Figures
Comment in
-
Gut microbiota is a hot and fast-moving topic, and paediatricians need to monitor the latest developments.Acta Paediatr. 2019 Nov;108(11):1934-1935. doi: 10.1111/apa.14960. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Acta Paediatr. 2019. PMID: 31490568 No abstract available.