Comparison of Immune Responses to Two Quadrivalent Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccines (CRM197 and Diphtheria Toxoid) in Healthy Adults
- PMID: 31197986
- PMCID: PMC6565927
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e169
Comparison of Immune Responses to Two Quadrivalent Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccines (CRM197 and Diphtheria Toxoid) in Healthy Adults
Abstract
Background: After the introduction of the meningococcal ACWY-CRM197 conjugate vaccine (MenACWY-CRM) in 2012 and the meningococcal ACWY-diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine (MenACWY-DT) in 2014, immunization was recommended for certain high-risk groups including new military recruits in Korea. However, comparative immunogenicity studies for these vaccines have not been performed in Korea. Here, we compared the immunogenicity of these two vaccines in healthy adults.
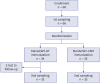
Methods: A total of 64 adults, 20-49 years of age, were randomly divided into two groups (1:1) to receive either of the two vaccines. The sera were obtained before and 1 month after vaccination and tested for serogroup-specific serum bactericidal activity using baby rabbit complement.
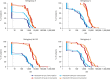
Results: There were no significant differences post-vaccination in the geometric mean indices and the seropositive rate to all serogroups between the vaccines. The proportion of seropositive subjects after vaccination ranged from 88% to 100%.
Conclusion: Both meningococcal conjugate vaccines showed good immunogenicity in healthy Korean adults without statistically significant differences. Further investigations for serotype distribution of circulating meningococci and the immune interference between other diphtheria toxin-containing vaccines concomitantly used for military recruits are needed to optimize immunization policies.
Trial registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0002460.
Keywords: Adult; Immunogenicity; Meningococcal Vaccines.
© 2019 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a booster dose of meningococcal (groups A, C, W, and Y) polysaccharide diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine.Vaccine. 2016 Oct 17;34(44):5273-5278. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.09.003. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27642132 Clinical Trial.
-
Immunogenicity of MenACWY-CRM in Korean Military Recruits: Influence of Tetanus-Diphtheria Toxoid Vaccination on the Vaccine Response to MenACWY-CRM.Yonsei Med J. 2016 Nov;57(6):1511-6. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1511. Yonsei Med J. 2016. PMID: 27593883 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Tdap upon antibody response to meningococcal polysaccharide when administered before, with or after the quadrivalent meningococcal TT-conjugate vaccine (coadministered with the 13-valent pneumococcal CRM197-conjugate vaccine) in adult Hajj pilgrims: A randomised controlled trial.Vaccine. 2018 Jul 5;36(29):4375-4382. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.04.033. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29880243 Clinical Trial.
-
MenACWY-TT vaccine for active immunization against invasive meningococcal disease.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012 May;11(5):523-37. doi: 10.1586/erv.12.32. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012. PMID: 22827239 Review.
-
An update of clinical experience with the quadrivalent meningococcal ACWY-CRM conjugate vaccine.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018 Oct;17(10):865-880. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2018.1521280. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018. PMID: 30198805 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-Marketing Surveillance Observational Study of Quadrivalent Meningococcal Diphtheria Toxoid Conjugate Vaccine (MenACWY-DT, MCV4/Menactra®) in the Republic of Korea, 2014-2019.Infect Dis Ther. 2021 Mar;10(1):399-409. doi: 10.1007/s40121-020-00393-4. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Infect Dis Ther. 2021. PMID: 33439463 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized study to evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of a pentavalent meningococcal vaccine.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Aug 7;9(1):140. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00935-8. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 39112515 Free PMC article.
-
Health care professionals' preference for a fully liquid, ready-to-use hexavalent vaccine in Spain.Prev Med Rep. 2021 Apr 16;22:101376. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2021.101376. eCollection 2021 Jun. Prev Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33996389 Free PMC article.
-
Serum bactericidal activity against meningococcus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025 May;68(5):362-369. doi: 10.3345/cep.2024.01151. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 39810504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harrison LH, Pass MA, Mendelsohn AB, Egri M, Rosenstein NE, Bustamante A, et al. Invasive meningococcal disease in adolescents and young adults. JAMA. 2001;286(6):694–699. - PubMed
-
- Rosenstein NE, Perkins BA, Stephens DS, Popovic T, Hughes JM. Meningococcal disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(18):1378–1388. - PubMed
-
- Thompson MJ, Ninis N, Perera R, Mayon-White R, Phillips C, Bailey L, et al. Clinical recognition of meningococcal disease in children and adolescents. Lancet. 2006;367(9508):397–403. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal S, Nadel S. Acute bacterial meningitis in infants and children: epidemiology and management. Paediatr Drugs. 2011;13(6):385–400. - PubMed
-
- Harrison LH, Trotter CL, Ramsay ME. Global epidemiology of meningococcal disease. Vaccine. 2009;27(Suppl 2):B51–B63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

