Structure and Function of the γ-Secretase Complex
- PMID: 31198028
- PMCID: PMC6618299
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00401
Structure and Function of the γ-Secretase Complex
Abstract
γ-Secretase is a membrane-embedded protease complex, with presenilin as the catalytic component containing two transmembrane aspartates in the active site. With more than 90 known substrates, the γ-secretase complex is considered "the proteasome of the membrane", with central roles in biology and medicine. The protease carries out hydrolysis within the lipid bilayer to cleave the transmembrane domain of the substrate multiple times before releasing secreted products. For many years, elucidation of γ-secretase structure and function largely relied on small-molecule probes and mutagenesis. Recently, however, advances in cryo-electron microscopy have led to the first detailed structures of the protease complex. Two new reports of structures of γ-secretase bound to membrane protein substrates provide great insight into the nature of substrate recognition and how Alzheimer's disease-causing mutations in presenilin might alter substrate binding and processing. These new structures offer a powerful platform for elucidating enzyme mechanisms, deciphering effects of disease-causing mutations, and advancing Alzheimer's disease drug discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Figures




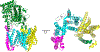


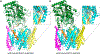

References
-
- Wolfe MS, De Los Angeles J, Miller DD, Xia W, and Selkoe DJ (1999) Are presenilins intramembrane-cleaving proteases? Implications for the molecular mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 38, 11223–11230. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe MS, and Kopan R (2004) Intramembrane proteolysis: theme and variations. Science 305, 1119–1123. - PubMed
-
- Hooper NM, and Lendeckel U, Eds. (2007) Intramembrane-Cleaving Proteases (I-CLiPs), Vol. 6, Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
-
- Freeman M (2014) The rhomboid-like superfamily: molecular mechanisms and biological roles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 30, 235–254. - PubMed
-
- Rawson RB (2013) The site-2 protease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr 1828, 2801–2807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

