Comparative Evaluation of Dexmedetomidine versus Midazolam as Premedication to Propofol Anesthesia in Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
- PMID: 31198249
- PMCID: PMC6545960
- DOI: 10.4103/aer.AER_62_19
Comparative Evaluation of Dexmedetomidine versus Midazolam as Premedication to Propofol Anesthesia in Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is used to diagnose and treat pancreaticobiliary diseases. It is a potentially uncomfortable procedure that needs to be performed under conscious sedation. Safe and effective sedation protocol is the need of an hour.
Aims: This study aims to evaluate the requirement of propofol using midazolam and dexmedetomidine as premedication for ERCP. The degree of comfort experienced by endoscopist and the patients was also assessed.
Materials and methods: A total of sixty patients were enrolled in a randomized, assessor-blinded study in the age group of 40-80 years, American Society of Anesthesiologists physical class II-III undergoing elective ERCP procedures. They were divided into two groups of 30 each. Group D (n = 30): Dexmedetomidine (100 μg/mL + 18 mL saline) loading dose at 1 μg/kg intravenous (IV) over 10 min followed by 0.5 μg/kg/h infusion, and Group M (n = 30): Midazolam at 0.05 mg/kg IV bolus over 10 min followed by normal saline infusion under hemodynamic monitoring. Satisfaction scores, total propofol requirement, and complications such as gagging, restlessness, agitation, postoperative nausea and vomiting were noted and analyzed statistically.
Statistical analysis: Statistical analysis was performed using SSPS 17.0 software (SPSS Inc., 233 South Wacker Drive, Chicago, USA). The Chi-square test was applied for nonparametric data and parametric numerical data, unpaired t-test for intergroup comparison, and repeated measures ANOVA for intragroup comparison. Results were expressed as a mean ± standard deviation. Value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant and <0.001 as highly significant.
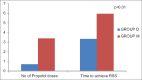
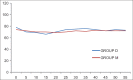
Results: Surgeons and patients were more satisfied and comfortable along with less requirement of propofol in the dexmedetomidine group. The incidence of complications was also less in the dexmedetomidine group as compared to that of midazolam group.
Conclusion: Both dexmedetomidine and midazolam can be safely administered as an anesthetic adjuvant to propofol for short procedures like ERCP's. Dexmedetomidine provided intense and better sedation quality along with lesser requirement of propofol doses. Moreover, it provided stable hemodynamic conditions and good recovery characteristics as compared to midazolam group.
Keywords: Conscious sedation; dexmedetomidine; endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; midazolam; propofol.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The dexmedetomidine "augmented" sedato analgesic cocktail: An effective approach for sedation in prolonged endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Apr-Jun;31(2):201-6. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.155149. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25948901 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol versus Dexmedetomidine for Sedation of Cancer Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: Randomized Single-Blinded Controlled Study.Anesth Pain Med. 2024 Sep 9;14(4):e148512. doi: 10.5812/aapm-148512. eCollection 2024 Aug. Anesth Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 40078472 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of a Dexmedetomidine-Remifentanil Combination Compared with a Midazolam-Remifentanil Combination for Conscious Sedation During Therapeutic Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography: A Prospective, Randomized, Single-Blinded Preliminary Trial.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Jun;63(6):1633-1640. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5034-3. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29594976 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Anesthetic and Sedative Regimens for Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Network Meta-Analysis.Dig Dis. 2025;43(1):84-95. doi: 10.1159/000542380. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Dig Dis. 2025. PMID: 39536718 Free PMC article.
-
A new view on old problems in paediatric anaesthesia: premedication, postoperative agitation and dosing.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2023 Jun 1;36(3):311-317. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000001236. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 36745083 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical usefulness of intermediate-dose dexmedetomidine (0.75 μg/kg) in flexible bronchoscopy - A prospective, randomized, double-blinded study.Indian J Pharmacol. 2021 Nov-Dec;53(6):440-447. doi: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_446_20. Indian J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34975131 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Perioperative Neurocognitive Dysfunction in Elderly Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Aug 23;18:3715-3725. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S470514. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39193191 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dexmedetomidine Versus Midazolam for Propofol Sparing in Procedural Sedation of Children With Leukemia: A Consecutive Case Series.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2025 Sep;69(8):e70107. doi: 10.1111/aas.70107. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2025. PMID: 40740101 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate Sedation or Deep Sedation for ERCP: What Are the Preferences in the Literature?Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 15;14(10):1306. doi: 10.3390/life14101306. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of midazolam and low-dose dexmedetomidine in flexible bronchoscopy: A prospective, randomized, double-blinded study.Indian J Pharmacol. 2020 Jan-Feb;52(1):23-30. doi: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_287_19. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Indian J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32201443 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Chen WX, Lin HJ, Zhang WF, Gu Q, Zhong XQ, Yu CH, et al. Sedation and safety of propofol for therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005;4:437–40. - PubMed
-
- Cotton PB. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: Maximizing benefits and minimizing risks. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2012;22:587–99. - PubMed
-
- Paspatis GA, Chainaki I, Manolaraki MM, Vardas E, Theodoropoulou A, Tribonias G, et al. Efficacy of bispectral index monitoring as an adjunct to propofol deep sedation for ERCP: A randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2009;41:1046–51. - PubMed