Comparison between the Effects of Sumatriptan Versus Naratriptan in the Treatment of Postdural Puncture Headache in Obstetric Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31198263
- PMCID: PMC6545953
- DOI: 10.4103/aer.AER_17_19
Comparison between the Effects of Sumatriptan Versus Naratriptan in the Treatment of Postdural Puncture Headache in Obstetric Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Postdural puncture headache (PDPH) in the obstetric anesthesia practice is one of the most annoying, common, and important problems.
Aim: This comparative study was designed to assess the efficacy of naratriptan in relieving PDPH in parturients who gave birth by cesarean section under intrathecal anesthesia and to compare its efficacy with sumatriptan.
Settings and design: One hundred and eighty-nine adult parturients who complained of PDPH in the first 3 days postpartum period were enrolled in this study. They were divided into three equal parallel groups of 63 each.
Materials and methods: Group-1 controlled (C-group) received multivitamin tablets, Group-2 sumatriptan (S-group) received sumatriptan tablets and Group-3 naratriptan (N-group) received naratriptan tablets. The efficacy of naratriptan in relieving PDPH was studied and compared with that of sumatriptan. Incidences of complications of both drugs were also noted.
Statistical analysis: The collected data were organized, tabulated, and statistically analyzed using SPSS software statistical computer package version 18 (SPSS Inc., USA).
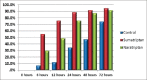
Results: After the first 6 h, there were statistically significant differences between Groups S and N from one side and control group from the other side (P < 0.0001 and 0.001), respectively, and the difference between Group S and Group N was statistically significant (P = 0.004). After 12 h, there were statistically significant differences between Groups S and N from one side and the control group from the other side (P < 0.0001) and the difference between Group S and Group N was statistically significant (P = 0.002). After 72 h, there were statistically significant differences between Groups S and N from one side and control group from the other side (P < 0.001 and 0.009), respectively. The difference was nonsignificant between S and N group (P = 0.717).
Conclusion: The study revealed that anti-migraine drug naratriptan in combination with supportive treatment was effective in relieving PDPH in parturients.
Keywords: Naratriptan; postdural puncture headache; spinal anesthesia; sumatriptan.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvants to Conventional Management of Postdural Puncture Headache Following Obstetric Surgery Under Spinal Anesthesia: Mirtazapine vs. Sumatriptan.Pain Physician. 2025 Jan;28(1):39-49. Pain Physician. 2025. PMID: 39903014 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of naratriptan and sumatriptan in recurrence-prone migraine patients. Naratriptan International Recurrence Study Group.Clin Ther. 2000 Aug;22(8):981-9. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(00)80069-7. Clin Ther. 2000. PMID: 10972634 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of naratriptan tablets in the acute treatment of migraine: a dose-ranging study. Naratriptan S2WB2004 Study Group.Clin Ther. 2000 Aug;22(8):970-80. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(00)80068-5. Clin Ther. 2000. PMID: 10972633 Clinical Trial.
-
Naratriptan is as effective as sumatriptan for the treatment of migraine attacks when used properly. A mini-review.Cephalalgia. 2021 Dec;41(14):1499-1505. doi: 10.1177/03331024211028959. Epub 2021 Jul 18. Cephalalgia. 2021. PMID: 34275352 Review.
-
Rational migraine management: optimising treatment with the triptans.Funct Neurol. 2000;15 Suppl 3:182-91. Funct Neurol. 2000. PMID: 11200789 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Propofol Anesthesia on the Pain Severity and Frequency of Migraine Attacks in Patients with Chronic Migraine Headache over a Six Month Follow Up: An Observational Study.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Fall;20(4):415-421. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2021.115243.15266. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 35194456 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Sumatriptan, Theophylline, Pregabalin and Caffeine on Prevention of Headache Caused By Spinal Anaesthesia (PDPH): A Systematic Review.J West Afr Coll Surg. 2022 Oct-Dec;12(4):102-116. doi: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_183_22. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2022. PMID: 36590776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Turnbull DK, Shepherd DB. Post-dural puncture headache: Pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Br J Anaesth. 2003;91:718–29. - PubMed
-
- Hayes NE, Wheelahan JM, Ross A. Self-reported post-discharge symptoms following obstetric neuraxial blockade. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2010;19:405–9. - PubMed
-
- Santanen U, Rautoma P, Luurila H, Erkola O, Pere P. Comparison of 27-gauge (0.41-mm) whitacre and quincke spinal needles with respect to post-dural puncture headache and non-dural puncture headache. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004;48:474–9. - PubMed
-
- Stella CL, Jodicke CD, How HY, Harkness UF, Sibai BM. Postpartum headache: Is your work-up complete? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196:318.e1–7. - PubMed