Developmental pathology of congenital kidney and urinary tract anomalies
- PMID: 31198539
- PMCID: PMC6543978
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfy112
Developmental pathology of congenital kidney and urinary tract anomalies
Abstract
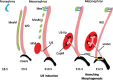
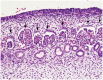
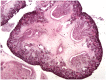
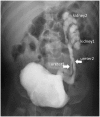
Congenital anomalies of the kidneys or lower urinary tract (CAKUT) are the most common causes of renal failure in children and account for 25% of end-stage renal disease in adults. The spectrum of anomalies includes renal agenesis; hypoplasia; dysplasia; supernumerary, ectopic or fused kidneys; duplication; ureteropelvic junction obstruction; primary megaureter or ureterovesical junction obstruction; vesicoureteral reflux; ureterocele; and posterior urethral valves. CAKUT originates from developmental defects and can occur in isolation or as part of other syndromes. In recent decades, along with better understanding of the pathological features of the human congenital urinary tract defects, researchers using animal models have provided valuable insights into the pathogenesis of these diseases. However, the genetic causes and etiology of many CAKUT cases remain unknown, presenting challenges in finding effective treatment. Here we provide an overview of the critical steps of normal development of the urinary system, followed by a description of the pathological features of major types of CAKUT with respect to developmental mechanisms of their etiology.
Keywords: CAKUT; congenital; development; genetics; kidney; urinary tract.
Figures
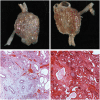

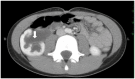
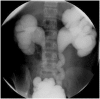
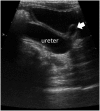
References
-
- Faa G, Gerosa C, Fanni C. et al. Morphogenesis and molecular mechanisms involved in human kidney development. J Cell Physiol 2012; 227: 1257–1268 - PubMed
-
- Saxen L. Inductive interactions in kidney development. Symp Soc Exp Biol 1971; 25: 207–221 - PubMed
-
- Weber S. Novel genetic aspects of congenital anomalies of kidney and urinary tract. Curr Opin Pediatr 2012; 24: 212–218 - PubMed
-
- Renkema KY, Winyard PJ, Skovorodkin IN. et al. Novel perspectives for investigating congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT). Nephrol Dial Transplant 2011; 26: 3843–3851 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

