Disease progression of alpha-mannosidosis and impact on patients and carers - A UK natural history survey
- PMID: 31198684
- PMCID: PMC6557729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.100480
Disease progression of alpha-mannosidosis and impact on patients and carers - A UK natural history survey
Abstract
Introduction: Alpha-mannosidosis is an ultra-rare lysosomal storage disorder resulting from the deficient activity of lysosomal alpha-mannosidase. Alpha-mannosidosis presents as a highly heterogenous condition with large variations in symptom severity and disease progression rates. Quantitative and qualitative data for alpha-mannosidosis patients and their caregivers provide important insights into their daily experiences.
Methods: A survey of nine alpha-mannosidosis patients was carried out in the UK between August 2017 and January 2018. Patient demographics, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and qualitative data from patients and carers relating to clinical characteristics and impact of the disease and treatment were analysed.
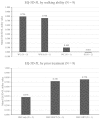
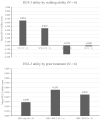
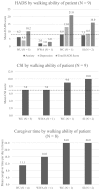
Results: At the time of survey completion, patient age ranged from 7 to 37 years. Five patients were described as 'walking unassisted', one as 'walking with assistance', one as 'wheelchair-dependent', and two as 'severely immobile'. In addition to best supportive care, three patients had received haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and one had received velmanase alfa enzyme replacement therapy (ERT). Patient HRQoL results for the EQ-5D-5 L questionnaire and the Health Utilities Index-3 showed that patients with more severe ambulatory health states reported lower utility values than patients who were more mobile. Patients who received HSCT or ERT experienced improved HRQoL. Carer HRQoL results for the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and Caregiver Strain Index demonstrated that carers experience high levels of stress and anxiety from their caregiving responsibilities.
Conclusions: This survey confirmed the heterogeneity of alpha-mannosidosis and the large impact of the disease and treatment on patients, carers, and families. Early diagnosis and access to treatment offers the best chance of slowing the disease progression and may provide some relief to patients and carers.
Keywords: Alpha-mannosidosis; Enzyme replacement therapy; Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Lysosomal storage disorder; Quality of life; Velmanase alfa.
Figures

References
-
- Meikle P.J., Hopwood J.J., Clague A.E., Carey W.F. Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA. 1999;281:249–254. - PubMed
-
- Prasad V.K., Kurtzberg J. Cord blood and bone marrow transplantation in inherited metabolic diseases: scientific basis, current status and future directions. Br. J. Haematol. 2010;148:356–372. - PubMed
-
- Ltd Chiesi. 2018. Lamzede Summary of Product Characteristics.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

