Complex regional pain syndrome-A forgotten entity
- PMID: 31198756
- PMCID: PMC6559117
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_193_19
Complex regional pain syndrome-A forgotten entity
Abstract
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is a painful condition characterized by regional pain that is disproportionate temporality and severity to the usual course of any known cause. The pain is regional which is not in a specific nerve territory or dermatomal distribution. Judicious clinical suspicion and targeted investigations are necessary for correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment. We hereby report a case of a young lady with CRPS who presented to us with unilateral upper limb pain, swelling, discoloration and muscle atrophy without any history of inciting injury.
Keywords: Bone scan; causalgia; complex regional pain syndrome; stellate ganglion blockade.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

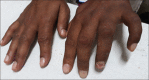
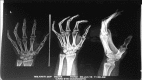
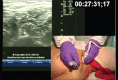
References
-
- Baron R, Levine JD, Fields HL. Causalgia and reflex sympathetic dystrophy: Does the sympathetic nervous system contribute to the generation of pain? Muscle Nerve. 1999;22:678–95. - PubMed
-
- Bruehl S. An update on the pathophysiology of complex regional pain syndrome. Anesthesiology. 2010;113:71325. - PubMed
-
- Harden RN, Oaklander AL, Burton AW, Perez RS, Richardson K, Swan M, et al. Complex regional pain syndrome: Practical diagnostic and treatment guidelines, 4th edition. Pain Med. 2013;14:180–229. - PubMed
-
- Bean DJ, Johnson MH, Heiss-Dunlop W, Lee AC, Kydd RR. Do psychological factors influence recovery from complex regional pain syndrome type 1? A prospective study. Pain. 2015;156:2310–8. - PubMed

