Distributed Tensor Decomposition for Large Scale Health Analytics
- PMID: 31198910
- PMCID: PMC6563812
- DOI: 10.1145/3308558.3313548
Distributed Tensor Decomposition for Large Scale Health Analytics
Abstract
In the past few decades, there has been rapid growth in quantity and variety of healthcare data. These large sets of data are usually high dimensional (e.g. patients, their diagnoses, and medications to treat their diagnoses) and cannot be adequately represented as matrices. Thus, many existing algorithms can not analyze them. To accommodate these high dimensional data, tensor factorization, which can be viewed as a higher-order extension of methods like PCA, has attracted much attention and emerged as a promising solution. However, tensor factorization is a computationally expensive task, and existing methods developed to factor large tensors are not flexible enough for real-world situations. To address this scaling problem more efficiently, we introduce SGranite, a distributed, scalable, and sparse tensor factorization method fit through stochastic gradient descent. SGranite offers three contributions: (1) Scalability: it employs a block partitioning and parallel processing design and thus scales to large tensors, (2) Accuracy: we show that our method can achieve results faster without sacrificing the quality of the tensor decomposition, and (3) FlexibleConstraints: we show our approach can encompass various kinds of constraints including l2 norm, l1 norm, and logistic regularization. We demonstrate SGranite's capabilities in two real-world use cases. In the first, we use Google searches for flu-like symptoms to characterize and predict influenza patterns. In the second, we use SGranite to extract clinically interesting sets (i.e., phenotypes) of patients from electronic health records. Through these case studies, we show SGranite has the potential to be used to rapidly characterize, predict, and manage a large multimodal datasets, thereby promising a novel, data-driven solution that can benefit very large segments of the population.
Keywords: Apache Spark; Distributed Algorithm; Health Analytics; Tensor Decomposition; User-Generated Content; Web Mining.
Figures
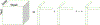
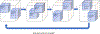
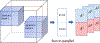
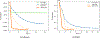


Similar articles
-
Communication Efficient Federated Generalized Tensor Factorization for Collaborative Health Data Analytics.Proc Int World Wide Web Conf. 2021 Apr;2021:171-182. doi: 10.1145/3442381.3449832. Proc Int World Wide Web Conf. 2021. PMID: 34467367 Free PMC article.
-
Logarithmic Norm Regularized Low-Rank Factorization for Matrix and Tensor Completion.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2021;30:3434-3449. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3061908. Epub 2021 Mar 9. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2021. PMID: 33651693
-
S3CMTF: Fast, accurate, and scalable method for incomplete coupled matrix-tensor factorization.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 28;14(6):e0217316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217316. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31251750 Free PMC article.
-
A Fused CP Factorization Method for Incomplete Tensors.IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. 2019 Mar;30(3):751-764. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2851612. Epub 2018 Jul 26. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. 2019. PMID: 30047907
-
Tensor Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis.J Med Signals Sens. 2024 Jul 10;14:16. doi: 10.4103/jmss.jmss_55_23. eCollection 2024. J Med Signals Sens. 2024. PMID: 39100745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Creating High-Quality Synthetic Health Data: Framework for Model Development and Validation.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Apr 22;8:e53241. doi: 10.2196/53241. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 38648097 Free PMC article.
-
Deep representation learning of patient data from Electronic Health Records (EHR): A systematic review.J Biomed Inform. 2021 Mar;115:103671. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2020.103671. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Biomed Inform. 2021. PMID: 33387683 Free PMC article.
-
Communication Efficient Federated Generalized Tensor Factorization for Collaborative Health Data Analytics.Proc Int World Wide Web Conf. 2021 Apr;2021:171-182. doi: 10.1145/3442381.3449832. Proc Int World Wide Web Conf. 2021. PMID: 34467367 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Diagnostics with Deep Forest Applied to Electronic Health Records.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;23(14):6571. doi: 10.3390/s23146571. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flu Season. [n. d.]. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flu_season.
-
- National Institutes of Health. [n. d.]. https://allofus.nih.gov/
-
- Acar Evrim, Dunlavy Daniel M, and Kolda Tamara G. 2011. A scalable optimization approach for fitting canonical tensor decompositions. Journal of Chemometrics 25, 2 (Feb. 2011), 67–86.
-
- Arango MF and Mejia-Mantilla JH. 2006. Magnesium for acute traumatic brain injury - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
